Effectiveness and Safety of iStent Infinite Trabecular Micro-Bypass for Uncontrolled Glaucoma
- PMID: 36260288
- PMCID: PMC9722368
- DOI: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000002141
Effectiveness and Safety of iStent Infinite Trabecular Micro-Bypass for Uncontrolled Glaucoma
Abstract
Prcis: The iStent Infinite Trabecular Micro-Bypass System implanted in patients with open angle glaucoma (OAG) (uncontrolled by prior surgical or medical therapy) was effective in reducing mean diurnal intraocular pressure with a favorable safety profile.
Purpose: The purpose of this study is to evaluate safety and effectiveness of the iStent infinite Trabecular Micro-Bypass System in patients with OAG uncontrolled by prior surgical or medical therapy.
Design: Prospective, multicenter, single-arm, open-label clinical trial.
Methods: Implantation of iStent infinite (3 iStent inject W stents) was performed as a stand-alone surgical procedure in eyes with OAG uncontrolled by prior incisional or cilioablative surgeries or maximum tolerated medical therapy (MTMT). Prospectively declared effectiveness endpoints were proportion of eyes achieving ≥20% mean diurnal intraocular pressure (MDIOP) reduction from baseline at month 12 on the same or fewer intraocular pressure (IOP)-lowering medication classes (responder endpoint) and mean change in MDIOP from baseline at month 12. Safety parameters included visual acuity, slit-lamp and fundus examinations, gonioscopy, perimetry, surgical complications, and adverse events.
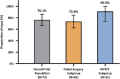
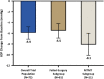
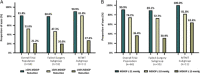
Results: Seventy-two eyes of 72 patients (mean age 71.9 y) with preoperative mean medicated MDIOP of 23.4±2.8 mm Hg on a mean of 3.1±0.9 IOP-lowering medication classes were enrolled: 61 eyes with failed prior surgery/ies (Failed-Surgery subgroup) and 11 eyes uncontrolled on MTMT (MTMT subgroup). A total of 76.1% of all enrolled patients met the responder endpoint (73.4% Failed-Surgery, 90.9% MTMT), with mean reduction (SE) in MDIOP at month 12 of 5.9(0.6) mm Hg [5.5(0.7) mm Hg Failed-Surgery subgroup, 8.1(0.9) mm Hg MTMT subgroup]. For patients on the same or fewer medication(s) as baseline, 53.0% achieved ≥30% MDIOP reduction without surgical interventions/other events. Safety was favorable, with no explants, infection, or device-related interventions or hypotony.
Conclusions: iStent infinite stand-alone surgery achieved clinically significant IOP reduction and favorable safety in patients with OAG uncontrolled by prior therapy.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Flaxman SR, Bourne RRA, Resnikoff S, et al. . Global causes of blindness and distance vision impairment 1990–2020: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2017;5:e1221–e1234. - PubMed
-
- Tham YCC, Li X, Wong TY, et al. . Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2014;121:2081–2090. - PubMed
-
- Heijl A, Leske MC, Bengtsson B, et al. . Reduction of intraocular pressure and glaucoma progression: results from the Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120:1268–1279. - PubMed
-
- Gordon MO, Beiser JA, Brandt JD, et al. . The ocular hypertension treatment study: baseline factors that predict the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120:714–720; discussion 829-30. - PubMed
-
- Chauhan BC, Mikelberg FS, Balaszi AG, et al. . Canadian glaucoma study: 2. risk factors for the progression of open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2008;126:1030–1036. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

