Evaluation of 4 prognostic indices in follicular lymphoma treated in first line with immunochemotherapy
- PMID: 36260737
- PMCID: PMC10173729
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022007949
Evaluation of 4 prognostic indices in follicular lymphoma treated in first line with immunochemotherapy
Abstract
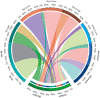
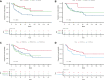
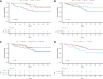
Several clinical risk models have been proposed to predict the outcome of follicular lymphoma (FL). The development of next-generation sequencing technologies has allowed the integration of somatic gene mutations into clinical scores to build genotyped-based risk models, such as the m7-Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (FLIPI). We explored 4 clinical or clinicogenetic-risk models in patients with symptomatic FL who received frontline immunochemotherapy. Of 191 patients with FL grades 1 to 3a, 109 were successfully genotyped. The treatment consisted of rituximab (R) plus cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CVP)/cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) (72.5%) or R-bendamustine (R-B) (27.5%). The proportion of cases classified as high risk for FLIPI, FLIPI-2, PRIMA-prognostic index, or m7-FLIPI were 39.3%, 14%, 30.3%, and 22%, respectively. No case with low-intermediate FLIPI was upgraded in the m7-FLIPI, but 18 of the 42 high-risk patients with FLIPI were downgraded to low-risk m7-FLIPI. The sensitivity and specificity for the prediction of POD24 were highest for FLIPI. The discrimination between progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) was the best for FLIPI (c-index: 0.644 and 0.727, respectively). When analyzed only in patients treated with R-B, m7-FLIPI showed a higher discrimination between PFS and OS. Thus, the FLIPI remains the clinical risk score with higher discrimination in patients with advanced FL treated with immunochemotherapy; however, the performance of the m7-FLIPI should be further investigated in patients treated with R-B.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.S. received research funding from Roche, AbbVie, and Gilead Sciences; served on speaker’s bureau for Roche and Janssen Pharmaceuticals; and provided consultancy for Janssen Pharmaceuticals and Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene. B.B. received research funding from Roche, AstraZeneca, and Novartis; provided consultancy for Thermo Fisher Scientific, Qiagen, Roche, AstraZeneca, Merck-Serono, Novartis, and Bristol Myers Squibb; and served on speaker’s bureau for Thermo Fisher Scientific, Qiagen, Roche, AstraZeneca, Biocartis, Merck-Serono, Novartis, and Bristol Myers Squibb. B.S. provided consultancy for Amgen, Novartis, and Takeda and served on speaker’s bureau for Amgen, Gilead Sciences, Novartis, Shire, and Takeda.
Figures

References
-
- Liu Q, Fayad L, Cabanillas F, et al. Improvement of overall and failure-free survival in stage IV follicular lymphoma: 25 years of treatment experience at the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(10):1582–1589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

