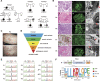
Clinical Implications of a New DDX58 Pathogenic Variant That Causes Lupus Nephritis due to RIG-I Hyperactivation
- PMID: 36261300
- PMCID: PMC10103098
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2022040477
Clinical Implications of a New DDX58 Pathogenic Variant That Causes Lupus Nephritis due to RIG-I Hyperactivation
Abstract
Background: Lupus nephritis (LN) is one of the most severe complications of systemic lupus erythematosus, with heterogeneous phenotypes and different responses to therapy. Identifying genetic causes of LN can facilitate more individual treatment strategies.
Methods: We performed whole-exome sequencing in a cohort of Chinese patients with LN and identified variants of a disease-causing gene. Extensive biochemical, immunologic, and functional analyses assessed the effect of the variant on type I IFN signaling. We further investigated the effectiveness of targeted therapy using single-cell RNA sequencing.
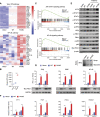
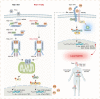
Results: We identified a novel DDX58 pathogenic variant, R109C, in five unrelated families with LN. The DDX58 R109C variant is a gain-of-function mutation, elevating type I IFN signaling due to reduced autoinhibition, which leads to RIG-I hyperactivation, increased RIG-I K63 ubiquitination, and MAVS aggregation. Transcriptome analysis revealed an increased IFN signature in patient monocytes. Initiation of JAK inhibitor therapy (baricitinib 2 mg/d) effectively suppressed the IFN signal in one patient.
Conclusions: A novel DDX58 R109C variant that can cause LN connects IFNopathy and LN, suggesting targeted therapy on the basis of pathogenicity.
Podcast: This article contains a podcast at.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Wu YL, Brookshire BP, Verani RR, Arnett FC, Yu CY: Clinical presentations and molecular basis of complement C1r deficiency in a male African-American patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 20: 1126–1134, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Al-Mayouf SM, Sunker A, Abdwani R, Abrawi SA, Almurshedi F, Alhashmi N, et al. : Loss-of-function variant in DNASE1L3 causes a familial form of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 43: 1186–1188, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Bilginer Y, Düzova A, Topaloğlu R, Batu ED, Boduroğlu K, Güçer Ş, et al. : Three cases of spondyloenchondrodysplasia (SPENCD) with systemic lupus erythematosus: A case series and review of the literature. Lupus 25: 760–765, 2016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

