Metformin improves tendon degeneration by blocking translocation of HMGB1 and suppressing tendon inflammation and senescence in aging mice
- PMID: 36262012
- PMCID: PMC10113400
- DOI: 10.1002/jor.25470
Metformin improves tendon degeneration by blocking translocation of HMGB1 and suppressing tendon inflammation and senescence in aging mice
Abstract
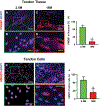
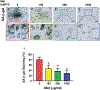
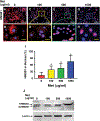
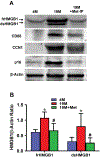
This study aimed to characterize aging-induced tendinopathy in mouse Achilles tendon and also to assess the treatment effects of metformin (Met) on aging tendon. We showed that compared to young tendon, aging tendon was in an inflammatory and senescent state as shown by increased expression of inflammatory disulfide HMGB1 (dsHMGB1), inflammatory macrophage marker CD68, and senescent cell markers SA-β-gal, p53, and p16. Moreover, aging tendon was degenerated marked by accumulation of proteoglycans and lipids in its interior. However, treatment of aging tendon by intraperitoneal (IP) injection of Met, a specific inhibitor of HMGB1, reduced dsHMGB1 levels, decreased the expression of CD68, SA-β-gal, CCN1, and p16 in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, Met treatment also increased the number of NS, SSEA-1, and CD73 positive stem cells in culture and improved the tendon structure in aging mouse. These findings of this study indicate that Met exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-senescent effects on aging tendon.
Keywords: HMGB1; aging; degeneration; inflammation; metformin; senescence; tendon.
© 2022 Orthopaedic Research Society. Published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures








References
-
- Colby SL, Ortman JM. 2015. Projections of the Size and Composition of the U.S. Population: 2014 to 2060. In: Commerce editor; pp. 1–13.
-
- Zhou B, Zhou Y, Tang K. 2014. An overview of structure, mechanical properties, and treatment for age-related tendinopathy. J Nutr Health Aging 18:441–448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

