Prognostic Signature GXYLT2 Is Correlated with Immune Infiltration in Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 36263004
- PMCID: PMC9576427
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5081413
Prognostic Signature GXYLT2 Is Correlated with Immune Infiltration in Bladder Cancer
Abstract
Background: GXYLT2 (glucoside xylosyltransferase 2) was known as an important gene that regulates classical Notch signaling and is involved in progression in human tumors. However, the correlation between GXYLT2 expression and bladder cancer remains unclear.
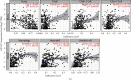
Methods: GXYLT2 expression was analyzed by ONCOMINE database, GEPIA database, and TIMER database. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) was utilized to confirm relationships between GXYLT2 and molecular subtypes of BLCA (bladder cancer). We discovered prognostic value of GXYLT2 in BLCA using GEPIA, LinkedOmics database, and Kaplan-Meier Plotter database. Subsequently, correlations between GXYLT2 and tumor immune infiltration were investigated through TIMER and TISIDB website. We then downloaded data of patients with BLCA from TCGA website, to conduct functional annotations and to construct protein-protein interaction network through STRING and Enrich web servers.
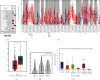
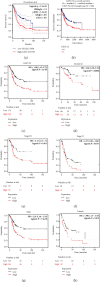
Results: Significant differences were observed between GXYLT2 expression of bladder cancer and normal tissues. GXYLT2 was a poor prognostic biomarker in BLCA with impact on diverse clinical characteristics. We found that GXYLT2 was closely related to tumor immune infiltrated cells and immune genes. Functional annotations indicated that GXYLT2 was linked to immune-related pathways.
Conclusions: The results suggested that GXYLT2 was associated with a poor prognosis and tumor immune cell infiltration of BLCA. GXYLT2 could be a promising therapeutic target in bladder cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Shuo Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

