Roles and mechanisms of garlic and its extracts on atherosclerosis: A review
- PMID: 36263122
- PMCID: PMC9574545
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.954938
Roles and mechanisms of garlic and its extracts on atherosclerosis: A review
Abstract
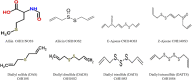
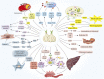
The prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) have achieved initial results, but the number of CVDs patients will increase rapidly in the next 10 years. Atherosclerosis (AS) is a significant risk factor for CVDs. The impact of lifestyle and daily diet varies considerably between different countries and continents and has been shown to affect the development of various diseases such as diabetes and CVDs. Primary and secondary prevention using alternative supplements and methods to avoid or reduce the use of traditional pharmacological drugs have also become popular. One of the reasons for this is that pharmacological drugs with lipid-lowering, and blood pressure-lowering effects cause many side effects that may negatively impact the quality of life. Patients are now emphasizing reliance on lifestyle changes to reduce cardiovascular risks. Garlic is a medicinal and edible plant that has been used for a long time. In order to reveal garlic application in the prevention and treatment of AS, reviewing the latest domestic and international studies through searching databases. The result shows that the antiatherogenic role of garlic is eximious. And the mechanisms are mainly related to hypolipidemic, antioxidant, antithrombotic, inhibiting angiogenesis, protecting endothelial cells, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, inhibiting vascular smooth muscle proliferation, and regulating gut microbiota. The main signaling pathways involve AMPK/TLRs, Keap1/Nrf2, PI3K/AKT, PPARγ/LXRα, GEF-H1/RhoA/Rac, etc. The antiatherogenic actions and molecular mechanism of garlic were reviewed in this study to obtain a robust evidence basis for the clinical application and mechanistic study and provide a theoretical basis for further utilization of garlic.
Keywords: Allium sativum; atherosclerosis; endothelial dysfunction; garlic; inflammation; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Yun, Wang, Li, Gao and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


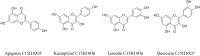
Similar articles
-
Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress.J Adv Res. 2021 Jul 6;34:43-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.023. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 35024180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Influence of Plants from the Alliaceae Family on Morphological Parameters of the Intestine in Atherogenic Rats.Nutrients. 2021 Oct 29;13(11):3876. doi: 10.3390/nu13113876. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34836133 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying the antihypertensive effects of garlic bioactives.Nutr Res. 2014 Feb;34(2):106-15. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2013.12.005. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Nutr Res. 2014. PMID: 24461311 Review.
-
Therapeutic effects of garlic in cardiovascular atherosclerotic disease.Chin J Nat Med. 2019 Oct;17(10):721-728. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(19)30088-3. Chin J Nat Med. 2019. PMID: 31703752 Review.
-
Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases with Anti-Inflammatory and Anti- Oxidant Nutraceuticals and Herbal Products: An Overview of Pre-Clinical and Clinical Studies.Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2018;12(2):145-157. doi: 10.2174/1872213X12666180815144803. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 30109827 Review.
Cited by
-
Two new and effective food-extracted immunomodulatory agents exhibit anti-inflammatory response activity in the hACE2 acute lung injury murine model of COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2024 May 14;15:1374541. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1374541. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38807598 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of garlic oil/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes and application.Front Nutr. 2023 Nov 29;10:1308787. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1308787. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38094921 Free PMC article.
-
Which Constituents Determine the Antioxidant Activity and Cytotoxicity of Garlic? Role of Organosulfur Compounds and Phenolics.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 1;25(15):8391. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158391. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125961 Free PMC article.
-
Garlic ameliorates atherosclerosis by regulating ferroptosis pathway: an integrated strategy of network pharmacology, bioinformatic and experimental verification.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 23;15:1388540. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1388540. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39108744 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomic analysis of the protective effect exerted by alliin on ox-LDL-injured HUVECs.Sci Rep. 2025 May 16;15(1):17072. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01677-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40379781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arellano-Buendía A. S., Castañeda-Lara L. G., Loredo-Mendoza M. L., García-Arroyo F. E., Rojas-Morales P., Argüello-García R., et al. fnm (2020). Effects of allicin on pathophysiological mechanisms during the progression of nephropathy associated to diabetes. Antioxidants (Basel, Switz. 9, 1134. 10.3390/antiox9111134 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

