Chinese medicinal herbs as potential prodrugs for obesity
- PMID: 36263142
- PMCID: PMC9573959
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1016004
Chinese medicinal herbs as potential prodrugs for obesity
Abstract
Obesity is a leading worldwide health threat with ever-growing prevalence, it promotes the incidence of various diseases, particularly cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, hypertension, and certain cancers. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has been used to control body weight and treat obesity for thousands of years, Chinese medicinal herbs provide a rich natural source of effective agents against obesity. However, some problems such as complex active ingredients, poor quality control, and unclear therapeutic mechanisms still need to be investigated and resolved. Prodrugs provide a path forward to overcome TCM deficiencies such as absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion (ADME) properties, and toxicity. This article aimed to review the possible prodrugs from various medicinal plants that demonstrate beneficial effects on obesity and seek to offer insights on prodrug design as well as a solution to the global obesity issues.
Keywords: active ingredient; bioavailability; herbal medicine; medicinal plants; nanotechnology; obesity; prodrug; traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).
Copyright © 2022 Law, Wang, Lu, Au, Chow, Leung and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
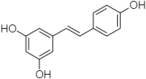

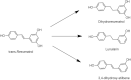









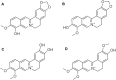



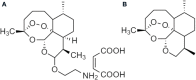
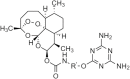
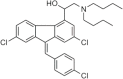
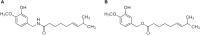

References
-
- Ahmed H. H., Kotob S. E., Abd-Rabou A. A., Aglan H. A., Elmegeed G. A., Mohawed O. A. (2021). Pre-clinical evidence for the anti-obesity potential of quercetin and curcumin loaded chitosan/PEG blended PLGA nanoparticles. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 14 (4), 1731–1759. 10.13005/bpj/2274 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

