Citrullinemia type I in Chinese children: Identification of two novel argininosuccinate synthetase gene mutations
- PMID: 36263152
- PMCID: PMC9574338
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.992156
Citrullinemia type I in Chinese children: Identification of two novel argininosuccinate synthetase gene mutations
Abstract
Background: In this study, we evaluated the clinical characteristics, prognosis, and gene mutations of five children with citrullinemia type I (CTLN1) diagnosed in our department and identified two novel ASS1 gene mutations.
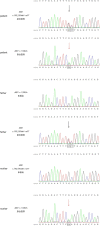
Methods: We examined the clinical characteristics, prognosis, and gene mutations of the five children through data collection, tandem mass spectrometry, and whole-exon sequencing. MutationTaster, regSNP-intron, and SWISS-MODEL were used for bioinformatic analysis to evaluate the two novel gene mutations. We analyzed differences in blood ammonia and citrulline levels based on clinical phenotypes. Finally, we reviewed the medical literature describing Chinese children with CTLN1.
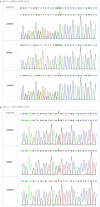
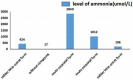
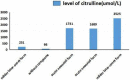
Results: ASS1 C773 + 6T > G and c.848 delA as well as c.952_953 del insTT and c.133G > A have not been previously reported in the Human Gene Mutation Database. Using MutationTaster and regSNP-intron, we predicted that these mutations affected protein function. The 3D structure obtained using SWISS-MODEL supported this prediction. Through comparative analysis showed that the ammonia level of the neonatal type was markedly higher than that of other types, whereas citrulline levels did not differ between groups.
Conclusion: We identified two novel mutations that cause disease. The blood ammonia level of neonatal form citrullinemia was markedly higher than that of other types. The genotype-phenotype association in Chinese patients remains unclear and should be further evaluated in genetic studies of larger sample sizes.
Keywords: argininosuccinate synthetase gene; citrullinemia type I; novel mutations; tandem mass spectrometry; whole-exome sequencing.
Copyright © 2022 Xiong and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Posset R, Garbade SF, Boy N, Burlina AB, Dionisi-Vici C, Dobbelaere D, et al. Transatlantic combined and comparative data analysis of 1095 patients with urea cycle disorders-a successful strategy for clinical research of rare diseases. J Inherit Metab Dis. (2019) 42:93–106. 10.1007/s10545-018-0222-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lyu Y, Song D, Wang W, Chen Y. ASS1 gene mutation in a neonate with citrullinemia type I. Basic Clin Med. (2020) 40:1403–6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

