Hepatic FGF21: Its Emerging Role in Inter-Organ Crosstalk and Cancers
- PMID: 36263162
- PMCID: PMC9576513
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.76924
Hepatic FGF21: Its Emerging Role in Inter-Organ Crosstalk and Cancers
Abstract
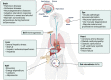
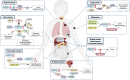
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 21 is one of the FGF members with special endocrine properties. In the last twenty years, it has attracted intense research and development for its physiological functions that respond to dietary manipulation, pharmacological benefits of improving the macronutrient metabolism, and clinical values as a biomarker of various human diseases. Generally, FGF21 can be produced by major metabolic organs, but only the subgroup from the liver shows canonical endocrine properties, which emphasizes the special value of delineating the unique secretory and functional characteristics of hepatic FGF21. There has been a growth in literature to address the extra-hepatic activities of FGF21, and many striking findings have therefore been published. Yet, they are fragmented and scattered, and controversies are raised from divergent findings. For this reason, there is a need for a systematic and critical evaluation of current research in this aspect. In this review, we focus on the current knowledge about the molecular biology of endocrine FGF21, especially present details on the regulation of circulating levels of FGF21. We also emphasize its emerging roles in inter-organ crosstalk and cancer development.
Keywords: Cancer; Endocrine FGF21; Fibroblast growth factor 21; Hepatic FGF21; Inter-organ crosstalk; Liver.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Nishimura T, Nakatake Y, Konishi M, Itoh N. Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2000;1492:203–6. - PubMed
-
- Badman MK, Pissios P, Kennedy AR, Koukos G, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E. Hepatic Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Is Regulated by PPARα and Is a Key Mediator of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in Ketotic States. Cell metabolism. 2007;5:426–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

