Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit ferroptosis and promote distant metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by upregulating ITGB3
- PMID: 36263165
- PMCID: PMC9576525
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.76162
Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit ferroptosis and promote distant metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by upregulating ITGB3
Abstract
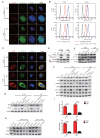
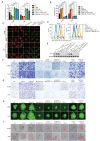
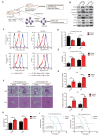
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a malignancy with high metastatic and invasive nature. Distant metastasis contributes substantially to treatment failure and mortality in NPC. Platelets are versatile blood cells and the number of platelets is positively associated with the distant metastasis of tumor cells. However, the role and underlying mechanism of platelets responsible for the metastasis of NPC cells remain unclear. Here we found that the distant metastasis of NPC patients was positively correlated with the expression levels of integrin β3 (ITGB3) in platelet-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) from NPC patients (P-EVs). We further revealed that EVs transfer occurred from platelets to NPC cells, mediating cell-cell communication and inducing the metastasis of NPC cells by upregulating ITGB3 expression. Mechanistically, P-EVs-upregulated ITGB3 increased SLC7A11 expression by enhancing protein stability and activating the MAPK/ERK/ATF4/Nrf2 axis, which suppressed ferroptosis, thereby facilitating the metastasis of NPC cells. NPC xenografts in mouse models further confirmed that P-EVs inhibited the ferroptosis of circulating NPC cells and promoted the distant metastasis of NPC cells. Thus, these findings elucidate a novel role of platelet-derived EVs in NPC metastasis, which not only improves our understanding of platelet-mediated tumor distant metastasis, but also has important implications in diagnosis and treatment of NPC.
Keywords: ITGB3; extracellular vesicles; ferroptosis; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; platelets.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
FLT1-enriched extracellular vesicles induce a positive feedback loop between nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells and endothelial cells to promote angiogenesis and tumour metastasis.Oncogene. 2025 Jul;44(27):2253-2267. doi: 10.1038/s41388-025-03389-x. Epub 2025 Apr 13. Oncogene. 2025. PMID: 40223024
-
EGFR-rich extracellular vesicles derived from highly metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells accelerate tumour metastasis through PI3K/AKT pathway-suppressed ROS.J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 Oct;10(1):e12003. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12003. Epub 2020 Oct 30. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 33304472 Free PMC article.
-
Four-dimensional trapped ion mobility spectrometry proteomics reveals circulating extracellular vesicles encapsulated drivers of nasopharyngeal carcinoma distant dissemination.Talanta. 2025 Jan 1;282:126907. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2024.126907. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Talanta. 2025. PMID: 39341061
-
The role of extracellular vesicles in the development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and potential clinical applications.Cancer Med. 2023 Jul;12(13):14484-14497. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6099. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37306659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of extracellular vesicles in circulating tumor cell-mediated distant metastasis.Mol Cancer. 2023 Nov 30;22(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01909-5. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38037077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Asparaginase and isoaspartyl peptidase 1 RNA interference suppresses the growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.Discov Oncol. 2024 Nov 9;15(1):636. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01228-1. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39520610 Free PMC article.
-
EMC2 suppresses ferroptosis via regulating TFRC in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Transl Oncol. 2025 Feb;52:102251. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102251. Epub 2024 Dec 21. Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39709720 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin β3-mediated platelet extracellular vesicle adhesion facilitates vascular smooth muscle cell dysfunction in postinjury intimal hyperplasia.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Mar 3;21(6):2380-2395. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.101391. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40303298 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicle-mediated ferroptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis: potential clinical applications in cancer therapy.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Jan 12;10(1):23. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01799-6. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38216595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dynamic role of platelets in cancer progression and their therapeutic implications.Nat Rev Cancer. 2024 Jan;24(1):72-87. doi: 10.1038/s41568-023-00639-6. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Nat Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38040850 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

