HDAC5-mediated Smad7 silencing through MEF2A is critical for fibroblast activation and hypertrophic scar formation
- PMID: 36263180
- PMCID: PMC9576526
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.76140
HDAC5-mediated Smad7 silencing through MEF2A is critical for fibroblast activation and hypertrophic scar formation
Abstract
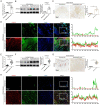
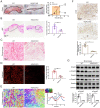
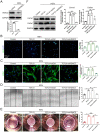
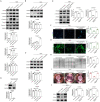
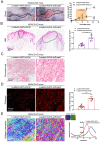
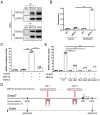
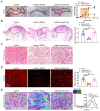
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling plays a key role in excessive fibrosis. As a class IIa family histone deacetylase (HDAC), HDAC5 shows a close relationship with TGF-β signaling and fibrosis. However, the effect and regulatory mechanism of HDAC5 in hypertrophic scar (HS) formation remain elusive. We show that HDAC5 was overexpressed in HS tissues and depletion of HDAC5 attenuated HS formation in vivo and inhibited fibroblast activation in vitro. HDAC5 knockdown (KD) significantly downregulated TGF-β1 induced Smad2/3 phosphorylation and increased Smad7 expression. Meanwhile, Smad7 KD rescued the Smad2/3 phosphorylation downregulation and scar hyperplasia inhibition mediated by HDAC5 deficiency. Luciferase reporter assays and ChIP-qPCR assays revealed that HDAC5 interacts with myocyte enhancer factor 2A (MEF2A) suppressing MEF2A binding to the Smad7 promoter region, which results in Smad7 promoter activity repression. HDAC4/5 inhibitor, LMK235, significantly alleviated hypertrophic scar formation. Our study provides clues for the development of HDAC5 targeting strategies for the therapy or prophylaxis of fibrotic diseases.
Keywords: HDAC5; Hypertrophic scar; MEF2A; Smad7; TGF-β.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Moortgat P, Meirte J, Maertens K, Lafaire C, De Cuyper L, Anthonissen M. Can a Cohesive Silicone Bandage Outperform an Adhesive Silicone Gel Sheet in the Treatment of Scars? A Randomized Comparative Trial. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2019;143:902–11. - PubMed
-
- Coentro JQ, Pugliese E, Hanley G, Raghunath M, Zeugolis DI. Current and upcoming therapies to modulate skin scarring and fibrosis. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2019;146:37–59. - PubMed
-
- Meng XM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Lan HY. TGF-beta: the master regulator of fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016;12:325–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

