Polymethylmethacrylate Membrane Dialyzer: Historic but Modern
- PMID: 36265445
- PMCID: PMC10210087
- DOI: 10.1159/000526996
Polymethylmethacrylate Membrane Dialyzer: Historic but Modern
Abstract
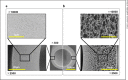
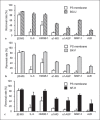
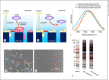
Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) hollow fiber membranes are one of the synthetic polymer hollow fiber membranes used to the hollow fiber artificial kidney. A PMMA hollow fiber membrane (PMMA membrane) has unique properties including the uniform structure and the adsorption property. Hemodialyzers using PMMA membranes, Filtryzer®, were approved in Japan in 1977 and have been used worldwide for over 40 years and so is a historical hemodialyzer.Various types in Filtryzer® having different pore sizes are developed and used in the clinical field. Filtryzer® B3 is a low-flux dialyzer. Filtryzer® BK has three types having different pore sizes, and above all, BK-F has the largest pores in the Filtryzer® series. Filtryzer® BG has a more uniform membrane structure by using weak anionic polymers compared with the earlier Filtryzer® series to remove β2-MG more. Filtryzer® NF is the latest Filtryzer® series and was developed as a dialyzer having improved antithrombogenicity compared with previous models and having protein adsorption property as the same with them. There have been many reports concerning Filtryzer® including improvement of patients' symptoms such as pruritus and nutrition on the advantages for dialysis patients. Although PMMA membranes are historic dialysis tools used for over 40 years, they are also modern dialysis membranes that have been updated to respond to dialysis therapy at those time.
Keywords: Adsorption; Filtryzer; Patient-reported outcomes; Polymethylmethacrylate; Polymethylmethacrylate hollow fiber membrane.
The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors, Yuichi Torii, Satoko Yamada, Mayumi Yajima, and Toru Sugata, are employed by the Toray Medical Corporation Limited.
Figures
References
-
- Liquori AM, Anzuino G, Coiro VM, D'Alagni M, de Santis P, Savino M. Complementary stereospecific interaction between isotactic and syndiotactic polymer molecules. Nature. 1965 Apr;206((4982)):358–362.
-
- Takeyama T, Sakay Y. Polymethylmethacrylate one biomaterial for a series of membrane. In: Ronco C, editor. Flexible membrane for a tailored dialysis. Contrib Nephrol. Vol. 125. Basel: Karger; 1999. pp. p. 9–24. - PubMed
-
- Sakai Y. Polymethylmethacrylate membrane with a series of serendipity. In: Saito A, Kawanishi H, Yamashita AC, Mineshima M, editors. High-Performance Membrane Dialyzers. Contrib Nephrol. Vol. 173. Basel: Karger; 2011. pp. p. 137–147. - PubMed
-
- Aucella F, Vigilante M, Gesuete A, Maruccio G, Specchio A, Gesualdo L. Uraemic itching do polymethylmethacrylate dialysis membranes play a role? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007 Jul;22((Suppl 5)):v8–v12. - PubMed
-
- Aoike I. Clinical significance of protein adsorbable membranes long-term clinical effects and analysis using a proteomic technique. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007 Jul;22((Suppl 5)):v13–v19. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

