RAD51AP1 regulates ALT-HDR through chromatin-directed homeostasis of TERRA
- PMID: 36265488
- PMCID: PMC9713952
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.09.025
RAD51AP1 regulates ALT-HDR through chromatin-directed homeostasis of TERRA
Abstract
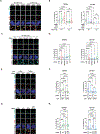
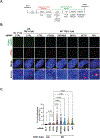
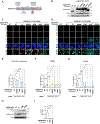
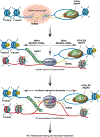
Alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) is a homology-directed repair (HDR) mechanism of telomere elongation that controls proliferation in subsets of aggressive cancer. Recent studies have revealed that telomere repeat-containing RNA (TERRA) promotes ALT-associated HDR (ALT-HDR). Here, we report that RAD51AP1, a crucial ALT factor, interacts with TERRA and utilizes it to generate D- and R-loop HR intermediates. We also show that RAD51AP1 binds to and might stabilize TERRA-containing R-loops as RAD51AP1 depletion reduces R-loop formation at telomere DNA breaks. Proteomic analyses uncover a role for RAD51AP1-mediated TERRA R-loop homeostasis in a mechanism of chromatin-directed suppression of TERRA and prevention of transcription-replication collisions (TRCs) during ALT-HDR. Intriguingly, we find that both TERRA binding and this non-canonical function of RAD51AP1 require its intrinsic SUMO-SIM regulatory axis. These findings provide insights into the multi-contextual functions of RAD51AP1 within the ALT mechanism and regulation of TERRA.
Keywords: ALT; RAD51AP1; TERRA; cancer; chromatin; homology-directed repair; telomere; transcription.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
TERRA and RAD51AP1 at the R&D-loop department of ALT telomeres.Mol Cell. 2022 Nov 3;82(21):3963-3965. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.10.006. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 36332602
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

