Diagnostic Technology for Spine Pathology
- PMID: 36266250
- PMCID: PMC9633243
- DOI: 10.31616/asj.2022.0374
Diagnostic Technology for Spine Pathology
Abstract
Diagnostic techniques for spinal pathologies have been developed in accordance with advances in technology. Accurate diagnosis of spinal pathology is essential for appropriate management of spinal diseases. Since the development of X-rays in 1895 and computed tomography (CT) in 1967, several diagnostic imaging modalities have been utilized for detecting spinal pathologies, including radiography, CT, magnetic resonance imaging, and radionuclide imaging. In addition to diagnostic imaging technologies, electrodiagnostic tests, including electromyography and nerve conduction studies, play a significant role as diagnostic tools, as spinal diseases are mostly profoundly associated with pathologies of the neural structures, such as the spinal cord and nerve root, and extent of injury at the structure cannot be adequately detected by conventional imaging techniques. In patient-specific treatment strategies, usage of diagnostic modalities is of great importance; thus, we should be aware of the basic details and approaches of the different diagnostic modalities. In this review, the authors discuss the details of the technologies that aid in the diagnosis of spinal pathologies.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Electrodiagnostic study; Images; Spinal diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
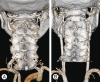

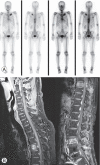
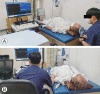
References
-
- Young IR. Significant events in the development of MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2004;20:183–6. - PubMed
-
- Kazamel M, Warren PP. History of electromyography and nerve conduction studies: a tribute to the founding fathers. J Clin Neurosci. 2017;43:54–60. - PubMed
-
- Dewing SB. Modern radiology in historical perspective. Springfield (IL): Charles C. Thomas;; 1962.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

