Comparative transcriptomics reveal different genetic adaptations of biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis isolate 1JN2 in response to Cd2+ treatment
- PMID: 36267191
- PMCID: PMC9577173
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1002482
Comparative transcriptomics reveal different genetic adaptations of biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis isolate 1JN2 in response to Cd2+ treatment
Abstract
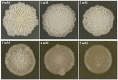
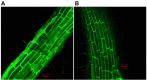
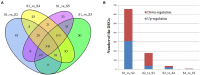
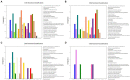
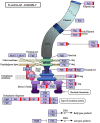
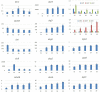
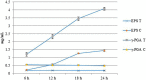
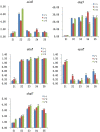
Biofilm plays important roles in the life cycle of Bacillus species, such as promoting host and object surface colonization and resisting heavy metal stress. This study utilized transcriptomics to evaluate the impacts of cadmium on the components, morphology, and function of biofilms of Bacillus subtilis strain 1JN2. Under cadmium ion stress, the morphology of the B. subtilis 1JN2 biofilm was flattened, and its mobility increased. Moreover, differential gene expression analysis showed that the main regulator of biofilm formation, Spo0A, decreased in expression under cadmium ion stress, thereby inhibiting extracellular polysaccharide synthesis through the SinI/SinR two-component regulatory system and the AbrB pathway. Cadmium ion treatment also increased the SigD content significantly, thereby increasing the expression of the flagella encoding and assembly genes in the strain. This promoted poly-γ-glutamic acid production via the DegS/DegU two-component regulatory system and the conversion of biofilm extracellular polysaccharide to poly-γ-glutamic acid. This conferred cadmium stress tolerance in the strain. Additionally, the cadmium ion-mediated changes in the biofilm composition affected the colonization of the strain on the host plant root surface. Cadmium ions also induced surfactin synthesis. These findings illustrate the potential of Bacillus species as biocontrol strains that can mitigate plant pathogenic infections and heavy metal stress. The results also provide a basis for the screening of multifunctional biocontrol strains.
Keywords: Bacillus subtilis; adaptation; biofilm; cadmium; stress response; transcriptomics analysis.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Yan, Dong, Li, Jiang, Gu, Niu, Zhou and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of biofilm formation by Cd2+ on Bacillus subtilis 1JN2 depressed its biocontrol efficiency against Ralstonia wilt on tomato.Microbiol Res. 2018 Oct;215:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2018.06.002. Epub 2018 Jun 2. Microbiol Res. 2018. PMID: 30172295
-
Comparative study of the role of surfactin-triggered signalling in biofilm formation among different Bacillus species.Microbiol Res. 2022 Jan;254:126920. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2021.126920. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Microbiol Res. 2022. PMID: 34800863
-
SpoVG is an important regulator of sporulation and affects biofilm formation by regulating Spo0A transcription in Bacillus cereus 0-9.BMC Microbiol. 2021 Jun 8;21(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02239-6. BMC Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34102998 Free PMC article.
-
The spo0A-sinI-sinR Regulatory Circuit Plays an Essential Role in Biofilm Formation, Nematicidal Activities, and Plant Protection in Bacillus cereus AR156.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2017 Aug;30(8):603-619. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-02-17-0042-R. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2017. PMID: 28430084
-
The Stress-Responsive Alternative Sigma Factor SigB of Bacillus subtilis and Its Relatives: An Old Friend With New Functions.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 15;11:1761. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01761. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33042030 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multimodal cadmium resistance and its regulatory networking in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain CD3.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):31689. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80754-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738119 Free PMC article.
-
Adding Metal Ions to the Bacillus mojavensis D50 Promotes Biofilm Formation and Improves Ability of Biocontrol.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Apr 28;9(5):526. doi: 10.3390/jof9050526. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37233237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almoneafy A. A., Kakar K. U., Nawaz Z., Li B., saand M. A., Chun-lan Y., et al. . (2014). Tomato plant growth promotion and antibacterial related-mechanisms of four rhizobacterial Bacillus strains against Ralstonia solanacearum. Symbiosis 63, 59–70. doi: 10.1007/s13199-014-0288-9 - DOI
-
- Alviz-Gazitua P., Fuentes-Alburquenque S., Rojas L. A., Turner R. J., Guiliani N., Seeger M. (2019). The response of Cupriavidus metallidurans CH34 to cadmium involves inhibition of the initiation of biofilm formation, decrease in intracellular c-di-GMP levels, and a novel metal regulated phosphodiesterase. Front. Microbiol. 10:1499. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01499, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

