Multiple asymptomatic papules following breast cancer treatment
- PMID: 36267823
- PMCID: PMC9580026
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.6447
Multiple asymptomatic papules following breast cancer treatment
Abstract
Acquired lymphangiectasia (AL) represents superficial lymphatic dilatation caused by different processes. It is a consequence of lymphatic damage by an external cause; leading to obstruction of local lymphatic drainage.1 We report a case of AL of the breast in a 45-year-old woman mimicking warts.
Keywords: acquired lymphangiectasia; breast cancer; dermoscopy; radiation therapy; warts.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

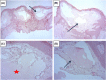
References
-
- Plotnick H, Richfield D. Tuberous lymphangiectatic varices secondary to radical mastectomy. AMA Arch Derm. 1956;74(5):466‐468. - PubMed
-
- Tasdelen I, Gokgoz S, Paksoy E, et al. Acquired lymphangiectasis after breast conservation treatment for breast cancer: report of a case. Dermatol Online J. 2004;10(1):9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

