The Comparative Pharmaco- and Histokinetics of the Therapeutic Dose of Estradiol Valerate and Bromocriptine in Common Quails
- PMID: 36267841
- PMCID: PMC9578813
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5482895
The Comparative Pharmaco- and Histokinetics of the Therapeutic Dose of Estradiol Valerate and Bromocriptine in Common Quails
Retraction in
-
Retracted: The Comparative Pharmaco- and Histokinetics of the Therapeutic Dose of Estradiol Valerate and Bromocriptine in Common Quails.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9814621. doi: 10.1155/2024/9814621. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38229992 Free PMC article.
Abstract
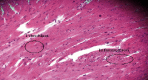
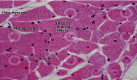
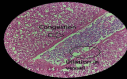
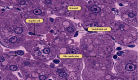
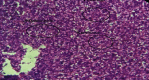
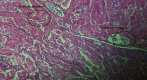
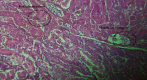
The current study is aimed at examining the overall effects of steroids on the tissues of organisms and pharmacotherapeutics and pharmaco-histokinetics of several steroids, including Bromocriptine as mesylate and estradiol valerate in common quails (Coturnix coturnix). A total of 100 birds were used for pharmaco-histokinetics. The research was carried out in two separate trials, one during the fall season and the other during the spring season. Each experiment lasted for five, ten, fifteen, and twenty days. Each study group used 20 birds while basing their experiments on a control group of 5. At the stretch of five, ten, fifteen, and twenty days in each season, therapeutic dosages were administered to a sum of two groups representing two separate steroid trial groups. Each steroid was administered to each bird in a therapeutic dose, which was three drops administered twice daily. Clinical symptoms include despondency, sluggishness, and variations in weight and temperature that almost all treated birds display. However, only in trials conducted in the fall was a sizable degree of body enlargement in one treated bird noticed. The winter testing showed a mortality rate. Four birds have died in the twenty-day group. One bird died when treated with estradiol valerate, and three birds died treated with Bromocriptine as mesylate. Both the male and female birds showed signs of having lost some of their body weight. The treated birds' kidney, stomach, hearts, and livers exhibited some edema. In comparison, almost all birds show enteritis, which indicates that steroids mainly affect the intestine. There were apparent differences in the histological analysis of heart and skeletal muscle and some treated birds with the control group. The kidney, liver, and intestine show the major histopathological change in all treated birds.
Copyright © 2022 Muhammad Nadeem et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Domínguez R., Flores A., Cruz-Morales S. E. Hormonal and neural mechanisms regulating hormone steroids secretion. Steroids Basic Science . 2012;3:p. 32. doi: 10.5772/29314. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

