Recent advances in small-molecular therapeutics for COVID-19
- PMID: 36268466
- PMCID: PMC9579963
- DOI: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbac024
Recent advances in small-molecular therapeutics for COVID-19
Abstract
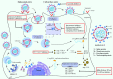
The COVID-19 pandemic poses a fundamental challenge to global health. Since the outbreak of SARS-CoV-2, great efforts have been made to identify antiviral strategies and develop therapeutic drugs to combat the disease. There are different strategies for developing small molecular anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs, including targeting coronavirus structural proteins (e.g. spike protein), non-structural proteins (nsp) (e.g. RdRp, Mpro, PLpro, helicase, nsp14, and nsp16), host proteases (e.g. TMPRSS2, cathepsin, and furin) and the pivotal proteins mediating endocytosis (e.g. PIKfyve), as well as developing endosome acidification agents and immune response modulators. Favipiravir and chloroquine are the anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents that were identified earlier in this epidemic and repurposed for COVID-19 clinical therapy based on these strategies. However, their efficacies are controversial. Currently, three small molecular anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents, remdesivir, molnupiravir, and Paxlovid (PF-07321332 plus ritonavir), have been granted emergency use authorization or approved for COVID-19 therapy in many countries due to their significant curative effects in phase III trials. Meanwhile, a large number of promising anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug candidates have entered clinical evaluation. The development of these drugs brings hope for us to finally conquer COVID-19. In this account, we conducted a comprehensive review of the recent advances in small molecule anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents according to the target classification. Here we present all the approved drugs and most of the important drug candidates for each target, and discuss the challenges and perspectives for the future research and development of anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs.
Keywords: COVID-19; Mpro inhibitor; RdRp inhibitor; SARS-CoV-2; host-targeted inhibitor; small molecule.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the West China School of Medicine & West China Hospital of Sichuan University.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Reveals High Sequence and Structural Conservation Prior to the Introduction of Protease Inhibitor Paxlovid.mBio. 2022 Aug 30;13(4):e0086922. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00869-22. Epub 2022 Jul 13. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35862764 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Docking Reveals Ivermectin and Remdesivir as Potential Repurposed Drugs Against SARS-CoV-2.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jan 25;11:592908. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.592908. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33746908 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into antiviral mechanisms of remdesivir, lopinavir/ritonavir and chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine affecting the new SARS-CoV-2.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;131:110668. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110668. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32861965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of Tox21 Screening Data to Evaluate the COVID-19 Drug Candidates for Their Potential Toxic Effects and Related Pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 14;13:935399. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.935399. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35910344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico study of novel niclosamide derivatives, SARS-CoV-2 nonstructural proteins catalytic residue-targeting small molecules drug candidates.Arab J Chem. 2023 May;16(5):104654. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.104654. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Arab J Chem. 2023. PMID: 36777994 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Analogs of the Catechol Derivative Dynasore Inhibit HIV-1 Ribonuclease H, SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 Exoribonuclease, and Virus Replication.Viruses. 2023 Jul 13;15(7):1539. doi: 10.3390/v15071539. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37515225 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Screening of an In-House Library of Structurally Distinct Chemotypes Towards the Identification of Novel SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitors.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Dec 11;17(12):1668. doi: 10.3390/ph17121668. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770510 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world effectiveness of azvudine for patients infected with the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA.5 in an intensive care unit.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Sep 28;15(9):4925-4937. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1093. Epub 2023 Sep 25. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 37868850 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors.Curr Clin Microbiol Rep. 2024 Sep;11(3):127-139. doi: 10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Curr Clin Microbiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39559548 Free PMC article.
-
Antimalarial compounds exhibit variant- and cell-type-specific activity against SARS-CoV-2 isolated in Panama.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 4;16:1537053. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1537053. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40535766 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous