Brain insulin resistance and cognitive function: influence of exercise
- PMID: 36269295
- PMCID: PMC9744647
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00375.2022
Brain insulin resistance and cognitive function: influence of exercise
Abstract
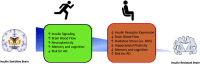
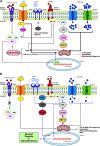
Exercise has systemic health benefits in people, in part, through improving whole body insulin sensitivity. The brain is an insulin-sensitive organ that is often underdiscussed relative to skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue. Although brain insulin action may have only subtle impacts on peripheral regulation of systemic glucose homeostasis, it is important for weight regulation as well as mental health. In fact, brain insulin signaling is also involved in processes that support healthy cognition. Furthermore, brain insulin resistance has been associated with age-related declines in memory and executive function as well as Alzheimer's disease pathology. Herein, we provide an overview of brain insulin sensitivity in relation to cognitive function from animal and human studies, with particular emphasis placed on the impact exercise may have on brain insulin sensitivity. Mechanisms discussed include mitochondrial function, brain growth factors, and neurogenesis, which collectively help combat obesity-related metabolic disease and Alzheimer's dementia.
Keywords: executive function; intranasal insulin; memory; mitochondrial function; physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity among adults: United States, 2017–2018. NCHS Data Brief 360: 1–8, 2020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

