Effects of fentanyl administration in mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36271330
- PMCID: PMC9585711
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-022-01871-7
Effects of fentanyl administration in mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Fentanyl is selected to manage pain in critical care patients on mechanical ventilation in the intensive care unit (ICU). However, the usefulness of fentanyl compared with other opioids is unknown. This study examined the evidence for using fentanyl to improve the clinical outcomes of ICU patients, using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) system.
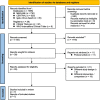
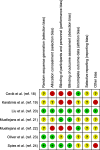
Methods: We searched the MEDLINE, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and Igaku Chuo Zasshi databases in June 2021. Two independent assessors reviewed studies to identify randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the intravenous administration of fentanyl and other opioids in mechanically ventilated patients in the ICU. The study quality was assessed using the GRADE system and Cochrane methodology. The primary outcome was mortality. The secondary outcomes were the duration of mechanical ventilation, duration of the ICU stay, incidence of severe adverse events, and incidence of delirium. We integrated outcome data using a random-effects model and showed absolute values and certainty of evidence in the GRADE evidence profile.
Results: Seven RCTs met the study inclusion criteria with 534 patients (251 were treated with fentanyl and 283 with other opioids, including 242 with remifentanil and 41 with morphine). Among 191 participants from 2 RCTs, fentanyl was not associated with mortality (risk ratio [RR], 0.79; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.24 to 2.60; low-quality evidence). Regarding the secondary outcomes, fentanyl did not shorten the duration of mechanical ventilation (mean difference, 0.49 h; 95% CI, - 0.90 to 1.88; moderate-quality evidence) or the duration of the ICU stay (mean difference, 7.04 h; 95% CI, - 3.27 to 17.35; moderate-quality evidence) compared with other opioids. Fentanyl did not increase the incidence of severe adverse events (RR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.50 to 1.90; low-quality evidence) or delirium (RR, 1.27; 95% CI, 0.79 to 2.04; low-quality evidence).
Conclusions: Although fentanyl is a frequently administered opioid in the ICU, patients' outcomes are not different between fentanyl use and use of other opioids. However, the GRADE evaluation provides little certainty to support the results of this systematic review. Therefore, further large RCTs are required to confirm our conclusions.
Trial registration: PROSPERO, CRD42019130648 ( https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=130648 ).
Keywords: Fentanyl; Mechanical ventilation; Morphine; Opioid; Remifentanil.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Opioids for newborn infants receiving mechanical ventilation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 17;3(3):CD013732. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013732.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33729556 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for preventing intensive care unit delirium in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 23;11(11):CD009783. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009783.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30484283 Free PMC article.
-
Protocol-directed sedation versus non-protocol-directed sedation in mechanically ventilated intensive care adults and children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 12;11(11):CD009771. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009771.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30480753 Free PMC article.
-
[Methohexital for analgosedation of ventilated intensive care patients : prospective nonrandomized single center observational study on incidence of delirium].Anaesthesist. 2014 Jun;63(6):488-95. doi: 10.1007/s00101-014-2317-8. Epub 2014 May 14. Anaesthesist. 2014. PMID: 24820355 German.
-
Effect of dexmedetomidine on delirium during sedation in adult patients in intensive care units: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Anesth. 2021 May;69:110157. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2020.110157. Epub 2020 Dec 3. J Clin Anesth. 2021. PMID: 33296787
Cited by
-
Evolution of Fentanyl Prescription Patterns and Administration Routes in Primary Care in Salamanca, Spain: A Comprehensive Analysis from 2011 to 2022.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Aug 14;12(16):1619. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12161619. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39201177 Free PMC article.
-
Remifentanil Versus Fentanyl in Critically Ill Patients Requiring Mechanical Ventilation: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study.Cureus. 2025 Jul 13;17(7):e87804. doi: 10.7759/cureus.87804. eCollection 2025 Jul. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40661821 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram for predicting delirium in the ICU among older patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.BMC Geriatr. 2025 May 28;25(1):383. doi: 10.1186/s12877-025-06049-7. BMC Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 40437405 Free PMC article.
-
Potentially inappropriate medications with older people in intensive care and associated factors: a historic cohort study.Sao Paulo Med J. 2023 Jul 31;142(1):e2022666. doi: 10.1590/1516-3180.2022.0666.R1.190523. eCollection 2023. Sao Paulo Med J. 2023. PMID: 37531493 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy of remifentanil and fentanyl in mechanically ventilated ICU patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis on ventilation duration and delirium incidence.J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2025 Jun 22;5(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s44158-025-00258-7. J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2025. PMID: 40544288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elliott D, Davidson JE, Harvey MA, Bemis-Dougherty A, Hopkins RO, Iwashyna TJ, et al. Exploring the scope of post-intensive care syndrome therapy and care: engagement of non-critical care providers and survivors in a second stakeholders meeting. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:2518–2526. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000525. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Devlin JW, Skrobik Y, Gélinas C, Needham DM, Slooter AJC, Pandharipande PP, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and management of pain, agitation/sedation, delirium, immobility, and sleep disruption in adult patients in the ICU. Crit Care Med. 2018;46:e825–e873. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003299. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

