A chromosome-level genome of Semiothisa cinerearia provides insights into its genome evolution and control
- PMID: 36271350
- PMCID: PMC9585740
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-022-08949-z
A chromosome-level genome of Semiothisa cinerearia provides insights into its genome evolution and control
Abstract
Background: Semiothisa cinerearia belongs to Geometridae, which is one of the most species-rich families of lepidopteran insects. It is also one of the most economically significant pests of the Chinese scholar tree (Sophora japonica L.), which is an important urban greenbelt trees in China due to its high ornamental value. A genome assembly of S. cinerearia would facilitate study of the control and evolution of this species.
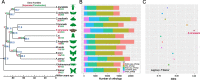
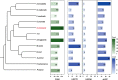
Results: We present a reference genome for S. cinerearia; the size of the genome was ~ 580.89 Mb, and it contained 31 chromosomes. Approximately 43.52% of the sequences in the genome were repeat sequences, and 21,377 protein-coding genes were predicted. Some important gene families involved in the detoxification of pesticides (P450) have expanded in S. cinerearia. Cytochrome P450 gene family members play key roles in mediating relationships between plants and insects, and they are important in plant secondary metabolite detoxification and host-plant selection. Using comparative analysis methods, we find positively selected gene, Sox15 and TipE, which may play important roles during the larval-pupal metamorphosis development of S. cinerearia.
Conclusion: This assembly provides a new genomic resource that will aid future comparative genomic studies of Geometridae species and facilitate future evolutionary studies on the S. cinerearia.
Keywords: Cytochrome P450; Geometridae; Semiothisa cinerearia; tipE.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The complete mitochondrial genome of Semiothisa cinerearia Bremer & Grey 1853 (Lepidoptera: Geometridae: Ennominae) and its phylogenetic analysis.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2023 Nov 14;8(11):1248-1252. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2023.2278820. eCollection 2023. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2023. PMID: 38188431 Free PMC article.
-
The Female-Biased General Odorant Binding Protein 2 of Semiothisa cinerearia Displays Binding Affinity for Biologically Active Host Plant Volatiles.Biology (Basel). 2024 Apr 18;13(4):274. doi: 10.3390/biology13040274. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38666886 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of chemosensory genes in Semiothisa cinerearia reveals sex-specific contributions for type-II sex pheromone chemosensation.Genomics. 2020 Nov;112(6):3846-3855. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.06.042. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32619572
-
Diversification of P450 genes during land plant evolution.Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2010;61:291-315. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112305. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2010. PMID: 20192745 Review.
-
Comparative analysis of the detoxification gene inventory of four major Spodoptera pest species in response to xenobiotics.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Nov;138:103646. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2021.103646. Epub 2021 Aug 29. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34469782 Review.
Cited by
-
The first complete mitochondrial genome of the agricultural pest Micromelalopha sieversi (Staudinger, 1892) (Lepidoptera: Notodontidae).Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2024 Jan 8;9(1):50-54. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2023.2301005. eCollection 2024. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2024. PMID: 38197053 Free PMC article.
-
A high-quality chromosome-level genome assembly of the mulberry looper, Phthonandria atrilineata.Sci Data. 2025 Jan 31;12(1):186. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-04509-8. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 39890890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zahiri R, Kitching IJ, Lafontaine JD, Mutanen M, Kaila L, Holloway JD, Wahlberg N. A new molecular phylogeny offers hope for a stable family level classification of the Noctuoidea (Lepidoptera) Zoolog Scr. 2011;40(2):158–173.
-
- Holloway JD. The moths of Borneo: Family geometridae, subfamilies sterrhinae and larentiinae. Malaynatj. 1997;51:1–242.
-
- Zhang L, Li S, Luo J, Du P, Wu L, Li Y, Zhu X, Wang L, Zhang S, Cui J. Chromosome-level genome assembly of the predator Propylea japonica to understand its tolerance to insecticides and high temperatures. Mol Ecol Resour. 2020;20(1):292–307. - PubMed
-
- Chen M, Mei Y, Chen X, Chen X, Xiao D, He K, Li Q, Wu M, Wang S, Zhang F, et al. A chromosome-level assembly of the harlequin ladybird Harmonia axyridis as a genomic resource to study beetle and invasion biology. Mol Ecol Resour. 2021;21(4):1318–1332. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

