Competing endogenous RNA networks related to prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: comprehensive analyses and construction of a novel risk score model
- PMID: 36271413
- PMCID: PMC9585723
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-022-00423-y
Competing endogenous RNA networks related to prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: comprehensive analyses and construction of a novel risk score model
Abstract
Background: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a heterogeneous B-cell malignancy that lacks specific biomarkers and drug targets. Competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) play vital roles in oncogenesis and tumor progression by sponging microRNAs (miRNAs). Nevertheless, the regulatory mechanisms of survival-related ceRNA networks in CLL remain to be uncovered.
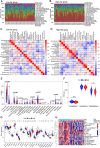
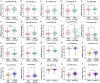
Methods: We included 865 de novo CLL patients to investigate RNA expression profiles and Illumina sequencing was performed on four CLL patients, two CLL cell lines and six healthy donors in our center. According to univariate Cox regression, LASSO regression as well as multivariate Cox regression analyses, we established a novel risk score model in CLL patients. Immune signatures were compared between the low- and high-risk groups with CIBERSORT and ESTIMATE program. Afterwards, we analyzed the relationship between differentially expressed miRNAs (DEmiRNAs) and IGHV mutational status, p53 mutation status and del17p. Based on the survival analyses and differentially expressed RNAs with targeting relationships, the lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA networks were constructed. In addition, the circRNA circ_0002078/miR-185-3p/TCF7L1 axis was verified and their interrelations were delineated by dual-luciferase reporter gene assay.
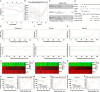
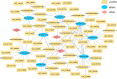
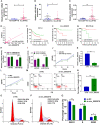
Results: Totally, 57 differentially expressed mRNAs (DEmRNAs) and 335 DEmiRNAs were identified between CLL patient specimens and normal B cells. A novel risk score model consisting of HTN3, IL3RA and NCK1 was established and validated. The concordance indexes of the model were 0.825, 0.719 and 0.773 in the training, test and total sets, respectively. The high-risk group was related to del(13q14) as well as shorter overall survival (OS). Moreover, we identified DEmiRNAs that related to cytogenetic abnormality of CLL patients, which revealed that miR-324-3p was associated with IGHV mutation, p53 mutation and del17p. The survival-related lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA networks were constructed to further facilitate the development of potential predictive biomarkers. Besides, the expression of circ_0002078 and TCF7L1 were significantly elevated and miR-185-3p was obviously decreased in CLL patients. Circ_0002078 regulated TCF7L1 expression by competing with TCF7L1 for miR-185-3p.
Conclusions: The comprehensive analyses of RNA expression profiles provide pioneering insights into the molecular mechanisms of CLL. The novel risk score model and survival-related ceRNA networks promote the development of prognostic biomarkers and potential therapeutic vulnerabilities for CLL.
Keywords: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia; Competing endogenous RNA; Non-coding RNAs; Prognostic biomarkers; Risk score model.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of immunity-related lncRNAs and construction of a ceRNA network of potential prognostic biomarkers in acute myeloid leukemia.Front Genet. 2023 Jun 14;14:1203345. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1203345. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37388937 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA network identifies four-lncRNA signature as a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer.J Transl Med. 2018 Sep 27;16(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1640-2. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30261893 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of circRNA-Based ceRNA Network to Reveal the Role of circRNAs in the Progression and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Genet. 2021 Feb 26;12:626764. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.626764. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33719338 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction and Analysis of the Differentially Expressed IncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019;29(6):539-549. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2019028740. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019. PMID: 32422009 Review.
-
Recent progress of prognostic biomarkers and risk scoring systems in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Biomark Res. 2020 Sep 7;8:40. doi: 10.1186/s40364-020-00222-3. eCollection 2020. Biomark Res. 2020. PMID: 32939265 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNAs regulate treatment outcome in leukemia: What have we learnt recently?Cancer Med. 2023 Jul;12(13):13966-13977. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6027. Epub 2023 May 6. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37148556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of PPARA as a Treatment Target for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.PPAR Res. 2023 Jun 26;2023:8456833. doi: 10.1155/2023/8456833. eCollection 2023. PPAR Res. 2023. PMID: 37404899 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNAs in acute myeloid leukemia: biomarkers, prognostic indicators, and treatment potential.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Apr 5;25(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03763-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40188050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: advances and challenges.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025 Apr 10;14(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s40164-025-00644-5. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40211406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in epigenetic alterations of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: from pathogenesis to treatment.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Mar 16;24(1):54. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01268-x. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38492089 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rozman C, Montserrat E. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(16):1052–1057. - PubMed
-
- Hallek M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2020 update on diagnosis, risk stratification and treatment. Am J Hematol. 2019;94(11):1266–1287. - PubMed
-
- Hombach S, Kretz M. Non-coding RNAs: Classification, Biology and Functioning. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;937:3–17. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

