Immunogenicity of a third dose of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in patients with CLL: effects on treatment selection
- PMID: 36271935
- PMCID: PMC9589533
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-022-05003-6
Immunogenicity of a third dose of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in patients with CLL: effects on treatment selection
Abstract
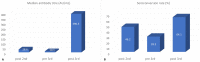
Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) show suboptimal responses to the vaccines against SARS-CoV-2; it has been shown though that a booster dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine may lead to a significant increase in the seroconversion rates of immunocompromised patients. We conducted a prospective, non-interventional study to evaluate the immunogenicity of a third dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine in adult patients with CLL. Sera were tested before the first, after the second, and before and after the third dose for anti-SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (RBD) spike protein IgG (anti-RBD). Thirty-nine patients with CLL were included in the study. The seroconversion rate increased from 28.2% before the third dose to 64.1% after the third dose and was higher in treatment-naïve patients (72.7% versus 47.1% in actively treated patients, p = 0.042). All but one patient achieving a seroconversion after the second dose retained after the third, while eight patients not achieving a seroconversion after the second dose (38.1%), did so after the third. Moreover, patients actively treated with venetoclax had a higher seroconversion rate than those treated with ibrutinib (87.5% versus 14.3%, p = 0.001). This study confirms the beneficial effect of a third dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine on the seroconversion rate in patients with CLL. Our results also strongly suggest that the use of venetoclax is correlated with higher immunogenicity/seroconversion rates than that of ibrutinib, a finding that has been reported by another study. A treatment strategy change during the pandemic favoring the use of venetoclax may be suggested based on our results, although these results should be validated in larger studies.
Keywords: BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine; Booster/3rd dose; Chronic lymphocytic leukemia; Ibrutinib; Venetoclax.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Muntañola A, Villacampa G, Hernández-Rivas J, Alonso R, Mirás F, Osorio S, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection in admitted patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia from a single European country. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2020;9(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40164-020-00195-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scarfò L, Chatzikonstantinou T, Rigolin GM, Quaresmini G, Motta M, Vitale C, et al. COVID-19 severity and mortality in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a joint study by ERIC, the European Research Initiative on CLL, and CLL Campus. Leukemia. 2020;34(9):2354–2363. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-0959-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

