Characterization of the binding of MRTX1133 as an avenue for the discovery of potential KRASG12D inhibitors for cancer therapy
- PMID: 36273239
- PMCID: PMC9588042
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-22668-1
Characterization of the binding of MRTX1133 as an avenue for the discovery of potential KRASG12D inhibitors for cancer therapy
Abstract
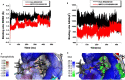
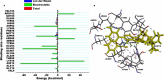
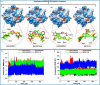
The Kirsten rat sarcoma (KRAS) oncoprotein has been on drug hunters list for decades now. Initially considered undruggable, recent advances have successfully broken the jinx through covalent inhibition that exploits the mutated cys12 in the switch II binding pocket (KRASG12C). Though this approach has achieved some level of success, patients with mutations other than cys12 are still uncatered for. KRASG12D is the most frequent KRAS mutated oncoprotein. It is only until recently, MRTX1133 has been discovered as a potential inhibitor of KRASG12D. This study seeks to unravel the structural binding mechanism of MRTX1133 as well as identify potential drug leads of KRASG12D based on structural binding characteristics of MRTX1133. It was revealed that MRTX1133 binding stabilizes the binding site by increasing the hydrophobicity which resultantly induced positive correlated movements of switches I and II which could disrupt their interaction with effector and regulatory proteins. Furthermore, MRTX1133 interacted with critical residues; Asp69 (- 4.54 kcal/mol), His95 (- 3.65 kcal/mol), Met72 (- 2.27 kcal/mol), Thr58 (- 2.23 kcal/mol), Gln99 (- 2.03 kcal/mol), Arg68 (- 1.67 kcal/mol), Tyr96 (- 1.59 kcal/mol), Tyr64 (- 1.34 kcal/mol), Gly60 (- 1.25 kcal/mol), Asp12 (- 1.04 kcal/mol), and Val9 (- 1.03 kcal/mol) that contributed significantly to the total free binding energy of - 73.23 kcal/mol. Pharmacophore-based virtual screening based on the structural binding mechanisms of MRTX1133 identified ZINC78453217, ZINC70875226 and ZINC64890902 as potential KRASG12D inhibitors. Further, structural optimisations and biochemical testing of these compounds would assist in the discovery of effective KRASG12D inhibitors.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Decoding KRAS dynamics: Exploring the impact of mutations and inhibitor binding.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2025 Feb;764:110279. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2024.110279. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39710177
-
Inside the cracked kernel: establishing the molecular basis of AMG510 and MRTX849 in destabilising KRASG12C mutant switch I and II in cancer treatment.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023 Jul;41(11):4890-4902. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2022.2074141. Epub 2022 May 11. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023. PMID: 35543250
-
Switch II Pocket Inhibitor Allosterically Freezes KRASG12D Nucleotide-binding Site and Arrests the GTPase Cycle.J Mol Biol. 2025 Jul 15;437(14):169162. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2025.169162. Epub 2025 Apr 21. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40268231
-
Next batter up! Targeting cancers with KRAS-G12D mutations.Trends Cancer. 2023 Nov;9(11):955-967. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2023.07.010. Epub 2023 Aug 15. Trends Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37591766 Review.
-
KRAS G12D targeted therapies for pancreatic cancer: Has the fortress been conquered?Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 29;12:1013902. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1013902. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36531078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The flavonoid Sudachitin regulates glucose metabolism via PDE inhibition.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 8;10(16):e35978. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35978. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39224336 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of novel carbazole hydrazine-carbothioamide scaffold as potent antioxidant, anticancer and antimicrobial agents.BMC Chem. 2024 May 21;18(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s13065-024-01207-1. BMC Chem. 2024. PMID: 38773663 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting drug-Protein interaction with deep learning framework for molecular graphs and sequences: Potential candidates against SAR-CoV-2.PLoS One. 2024 May 10;19(5):e0299696. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299696. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38728335 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing Andrographis paniculata leaves and roots by effective usage of the bioactive andrographolide and its nanodelivery: investigation of antikindling and antioxidant activities through in silico and in vivo studies.Front Nutr. 2023 May 31;10:1185236. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1185236. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37324729 Free PMC article.
-
DFT and molecular simulation validation of the binding activity of PDEδ inhibitors for repression of oncogenic k-Ras.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 8;19(3):e0300035. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300035. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38457483 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

