Functional consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection in pregnant women, fetoplacental unit, and neonate
- PMID: 36273675
- PMCID: PMC9581789
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2022.166582
Functional consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection in pregnant women, fetoplacental unit, and neonate
Abstract
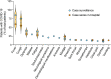
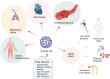
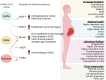
The SARS-CoV-2 infection causes COVID-19 disease, characterized by acute respiratory distress syndrome, bilateral pneumonia, and organ failure. The consequences of maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection for the pregnant woman, fetus, and neonate are controversial. Thus, it is required to determine whether there is viral and non-viral vertical transmission in COVID-19. The disease caused by SARS-CoV-2 leads to functional alterations in asymptomatic and symptomatic pregnant women, the fetoplacental unit and the neonate. Several diseases of pregnancy, including COVID-19, affect the fetoplacental function, which causes in utero programming for young and adult diseases. A generalized inflammatory state and a higher risk of infection are seen in pregnant women with COVID-19. Obesity, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension may increase the vulnerability of pregnant women to infection by SARS-CoV-2. Alpha, Delta, and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2 show specific mutations that seem to increase the capacity of the virus to infect the pregnant woman, likely due to increasing its interaction via the virus S protein and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors. This review shows the literature addressing to what extent COVID-19 in pregnancy affects the pregnant woman, fetoplacental unit, and neonate. Prospective studies that are key in managing SARS-CoV-2 infection in pregnancy are discussed.
Keywords: Covid-19; Fetus; Neonate; Placenta; Pregnancy; Virus.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Martins M.M., Alves da Cunha A.J.L., Robaina J.R., Raymundo C.E., Barbosa A.P., Medronho R.A. Fetal, neonatal, and infant outcomes associated with maternal zika virus infection during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2021;16 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246643. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

