Glutathione deficiency in the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection and its effects upon the host immune response in severe COVID-19 disease
- PMID: 36274722
- PMCID: PMC9582773
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.979719
Glutathione deficiency in the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection and its effects upon the host immune response in severe COVID-19 disease
Abstract
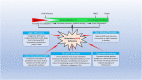
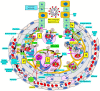
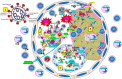
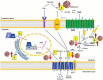
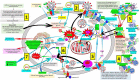
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that causes coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) has numerous risk factors leading to severe disease with high mortality rate. Oxidative stress with excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that lower glutathione (GSH) levels seems to be a common pathway associated with the high COVID-19 mortality. GSH is a unique small but powerful molecule paramount for life. It sustains adequate redox cell signaling since a physiologic level of oxidative stress is fundamental for controlling life processes via redox signaling, but excessive oxidation causes cell and tissue damage. The water-soluble GSH tripeptide (γ-L-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-glycine) is present in the cytoplasm of all cells. GSH is at 1-10 mM concentrations in all mammalian tissues (highest concentration in liver) as the most abundant non-protein thiol that protects against excessive oxidative stress. Oxidative stress also activates the Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1)-Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-antioxidant response element (ARE) redox regulator pathway, releasing Nrf2 to regulate the expression of genes that control antioxidant, inflammatory and immune system responses, facilitating GSH activity. GSH exists in the thiol-reduced and disulfide-oxidized (GSSG) forms. Reduced GSH is the prevailing form accounting for >98% of total GSH. The concentrations of GSH and GSSG and their molar ratio are indicators of the functionality of the cell and its alteration is related to various human pathological processes including COVID-19. Oxidative stress plays a prominent role in SARS-CoV-2 infection following recognition of the viral S-protein by angiotensin converting enzyme-2 receptor and pattern recognition receptors like toll-like receptors 2 and 4, and activation of transcription factors like nuclear factor kappa B, that subsequently activate nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase (NOX) expression succeeded by ROS production. GSH depletion may have a fundamental role in COVID-19 pathophysiology, host immune response and disease severity and mortality. Therapies enhancing GSH could become a cornerstone to reduce severity and fatal outcomes of COVID-19 disease and increasing GSH levels may prevent and subdue the disease. The life value of GSH makes for a paramount research field in biology and medicine and may be key against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; Glutathione; SARS-CoV-2; acute respiratory distress syndrome; atherosclerosis; atherothrombosis; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2022 Labarrere and Kassab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glutathione: A Samsonian life-sustaining small molecule that protects against oxidative stress, ageing and damaging inflammation.Front Nutr. 2022 Nov 1;9:1007816. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1007816. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36386929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf2 deficiency induces oxidative stress and promotes RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:789-799. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23954472
-
S-1-propenylmercaptocysteine protects murine hepatocytes against oxidative stress via persulfidation of Keap1 and activation of Nrf2.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Nov 1;143:164-175. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.07.022. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31349040
-
The thioredoxin antioxidant system.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Jan;66:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.036. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 23899494 Review.
-
Zinc ions as effectors of environmental oxidative lung injury.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:57-69. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.048. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23747928 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of oxidative stress on viral infections: an overview.Npj Viruses. 2025 Apr 12;3(1):27. doi: 10.1038/s44298-025-00110-3. Npj Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40295852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective.Life (Basel). 2025 Jan 16;15(1):113. doi: 10.3390/life15010113. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39860053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The peptidoglycan of Borrelia burgdorferi can persist in discrete tissues and cause systemic responses consistent with chronic illness.Sci Transl Med. 2025 Apr 23;17(795):eadr2955. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adr2955. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Sci Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40267217 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Glutathione in Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Induced Immunothrombosis and Cytokine Dysregulation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 22;13(3):271. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030271. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539805 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of N-acetylcysteine on lactate, biomarkers of oxidative stress, immune response, and muscle damage: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Dec;28(23):e70198. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70198. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39632267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ader F., Bouscambert-Duchamp M., Hites M., Peiffer-Smadja N., Poissy J., Belhadi D., et al. . (2022). Remdesivir plus standard of care versus standard of care alone for the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (dis CoVeRy): a phase 3, randomised, controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 22, 209–221. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00485-0, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

