Comparison of ultrasound-guided internal jugular vein cannulation versus supraclavicular approach to brachiocephalic vein cannulation- A prospective, single-blind, randomised study
- PMID: 36274805
- PMCID: PMC9580593
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.ija_948_21
Comparison of ultrasound-guided internal jugular vein cannulation versus supraclavicular approach to brachiocephalic vein cannulation- A prospective, single-blind, randomised study
Abstract
Background and aims: The internal jugular vein (IJV) is the most common site for central venous cannulation. Ultrasonography (USG)-guided brachiocephalic vein (BCV) cannulation has been described recently. The objective of this study was to compare the first attempt success rate, overall success rate and procedural ease between two techniques.
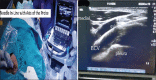
Methods: This was a prospective, single-blinded, randomised clinical study. Patients were randomly allocated into two groups using computer generated random table. Group IJV included 55 patients of USG-guided out-of-plane approach to the right IJV cannulation and group BCV included 55 patients for USG-guided supraclavicular in-plane approach to right BCV cannulation. The success rate, number of redirections needed, vein and needle tip visualisation, cannulation time and complication rate were compared between the groups.
Results: Demographic parameters were similar between the groups. Success rate of cannulation was 98.5% in IJV group and 100% in group BCV (P = 0.31). The first attempt success rate was 76.3% and 81.81% in IJV and BCV group, respectively (P = 0.42). IJV was collapsed in 14.5% cases and BCV was collapsed in 0.9% cases. The needle visualisation was better in BCV group (94.54%) compared to IJV (80%) (P = 0.02) group, which was statistically significant. The numbers of redirections of needle were more in IJV group. Thus the procedural ease was better with BCV than IJV.
Conclusion: Supraclavicular USG-guided in-plane BCV cannulation is a good alternative to USG-guided out-of-plane IJV cannulation, because of good calibre of the vein and better needle visualisation in the BCV group.
Keywords: Brachiocephalic veins; catheterisation; central venous; jugular veins; subclavian vein; ultrasonography.
Copyright: © 2022 Indian Journal of Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yonei A, Sari A. Real-time ultrasonic guidance for percutaneous puncture of the internal jugular vein. Anesthesiology. 1986;64:830–1. - PubMed
-
- Breschan C, Platzer M, Jost R, Stettner H, Beyer AS, Feigl G, et al. Consecutive, prospective case series of a new method for ultrasound-guided supraclavicular approach to the brachiocephalic vein in children. Br J Anaesth. 2011;106:732–7. - PubMed
-
- Mallin M, Louis H, Madsen T. A novel technique for ultrasound-guided supraclavicular subclavian cannulation. Am J Emerg Med. 2010;28:966–9. - PubMed
-
- Beccaria PF, Silvetti S, Lembo R, Landoni G, Monti G, Zambon M, et al. The brachiocephalic vein as a safe and viable alternative to internal jugular vein for central venous cannulation. Anesth Analg. 2018;127:146–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources