A Review of the Ultrathin Orsiro Biodegradable Polymer Drug-eluting Stent in the Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease
- PMID: 36274821
- PMCID: PMC9559229
- DOI: 10.17925/HI.2019.13.2.17
A Review of the Ultrathin Orsiro Biodegradable Polymer Drug-eluting Stent in the Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract
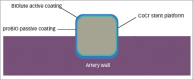
Drug-eluting stents (DES) have revolutionised the treatment of coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. In recent years, there has been a focus on a new generation of DES, such as biodegradable polymer DES (BP-DES). This novel stent platform was developed with the hope of eliminating the risk of very late stent thrombosis associated with the current gold-standard durable polymer DES (DP-DES). Ultrathin Orsiro BP-DES (Biotronik, Bülach, Switzerland) are based on a cobalt-chromium stent platform that is coated with a bioresorbable polymer coating containing sirolimus. These devices have one of the thinnest struts available in the current market and have the theoretical benefit of reducing a chronic inflammatory response in the vessel wall. In 2019, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of Orsiro BP-DES in patients with CAD based on promising results in recent landmark trials, such as BIOFLOW V and BIOSTEMI. The aim of the present review article was to discuss the history of stent technology and the continued opportunities for improvements, focusing on the potential benefits of Orsiro BP-DES.
Keywords: Biodegradable polymer; Orsiro; coronary artery disease; drug-eluting stents.
© Touch Medical Media 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: James J Wu, Joshua AH Way and David Brieger have nothing to declare in relation to this article.
Figures
References
-
- Kobo O, Roguin A.. Orsiro: ultrathin bioabsorbable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent. Future Cardiol. 2019;15:295–300. - PubMed
-
- Chen D, Jepson N. Coronary stent technology: a narrative review. Med J Aust. 2016;205:277–81. - PubMed
-
- Mueller RL, Sanborn TA. The history of interventional cardiology: cardiac catheterization, angioplasty, and related interventions. Am Heart J. 1995;129:146–72. - PubMed
-
- Castaneda WR, Formanek A, Tadavarthy M. et al. The mechanism of balloon angioplasty. Radiology. 1990;135:565–71. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous