Surgical procedures in infants with early diagnoses of developmental dysplasia of the hip. A prospective 4-year follow-up study
- PMID: 36275488
- PMCID: PMC9579446
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2022.09.021
Surgical procedures in infants with early diagnoses of developmental dysplasia of the hip. A prospective 4-year follow-up study
Abstract
Background: Dysplastic hips infants may normalize spontaneously without any intervention due to the natural growth. However, some infants need one or more surgical interventions to achieve stable and non-dysplastic hips. The purpose of this study is to determine the proportion of infants diagnosed with DDH before the age of 6 months undergoing surgical procedures of the hip(s) before the age of four years and to determine the number and types of surgical procedures in each infant.
Methods: A prospective and consecutive study of all infants aged 0-6 months diagnosed with dysplasia of the hips in the combined paediatric orthopaedic and radiologic examination in the Region of Southern Denmark 2013-2017. From medical records, we obtained information about all surgical procedures in the hips including open or closed reductions, arthrographies, tenotomies, and pelvic osteotomies before the age of 4 years.
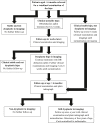
Results: Overall, 281 infants with hip dysplasia were included. The median age at first examination was 48 days. In 254 (90%) of the infants, the hips resolved spontaneously, and 27 (10%) needed one or more surgical interventions. Overall, the 27 infants had 47 surgical intervention as 12 infants had more than one intervention. One infants had five surgical interventions. The most frequent surgical procedures were closed reduction and arthrography with or without adductor tenotomy (58%) and pelvic osteotomy (27%). Among infants with surgical interventions, 23 (8.2%) had unstable hips, and four (1.4%) had stable hips. All four infants with stable hips had an arthrography and none required a pelvic osteotomy.
Discussion: This study supports the propensity for spontaneous normalization early dysplasia of the hips in infants. Only a small proportion of the infants needed surgical interventions to achieve stable and non-dysplastic hips.
Keywords: DDH; Developmental dysplasia of the hip; Infant; Surgery.
© 2022 Professor P K Surendran Memorial Education Foundation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cochrane Review: Screening programmes for developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborn infants.Evid Based Child Health. 2013 Jan;8(1):11-54. doi: 10.1002/ebch.1891. Evid Based Child Health. 2013. PMID: 23878122 Review.
-
A protocol for the use of closed reduction in children with developmental dysplasia of the hip incorporating open psoas and adductor releases and a short-leg cast: Mid-term outcomes in 113 hips.Bone Joint J. 2016 Nov;98-B(11):1548-1553. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.98B11.36606. Bone Joint J. 2016. PMID: 27803233
-
Developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants referred for a combined pediatric orthopedic and radiologic examination. A prospective cohort study.J Orthop. 2022 May 24;32:109-114. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2022.05.014. eCollection 2022 Jul-Aug. J Orthop. 2022. PMID: 35668834 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary Surgery and Residual Dysplasia Following Late Closed or Open Reduction of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021 Feb 3;103(3):235-242. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.20.00562. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021. PMID: 33252590
-
How Does Bony Surgery Affect Results of Anterior Open Reduction in Walking-age Children With Developmental Hip Dysplasia?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016 May;474(5):1199-208. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4598-x. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016. PMID: 26487045 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Biedermann R., Riccabona J., Giesinger J.M., et al. Results of universal ultrasound screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a prospective follow-up of 28 092 consecutive infants. Bone Joint Lett J. 2018;100-B(10):1399–1404. - PubMed
-
- Pollet V., Percy V., Prior H.J. Relative risk and incidence for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr. 2017;181:202–207. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials