Cytokine levels associated with favorable clinical outcome in the CAPSID randomized trial of convalescent plasma in patients with severe COVID-19
- PMID: 36275695
- PMCID: PMC9582990
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1008438
Cytokine levels associated with favorable clinical outcome in the CAPSID randomized trial of convalescent plasma in patients with severe COVID-19
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the profile of cytokines in patients with severe COVID-19 who were enrolled in a trial of COVID-19 convalescent plasma (CCP).
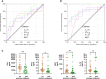
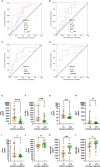
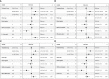
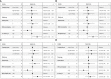
Methods: Patients were randomized to receive standard treatment and 3 CCP units or standard treatment alone (CAPSID trial, ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04433910). The primary outcome was a dichotomous composite outcome (survival and no longer severe COVID-19 on day 21). Time to clinical improvement was a key secondary endpoint. The concentrations of 27 cytokines were measured (baseline, day 7). We analyzed the change and the correlation between serum cytokine levels over time in different subgroups and the prediction of outcome in receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analyses and in multivariate models.
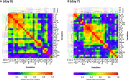
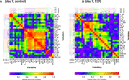
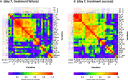
Results: The majority of cytokines showed significant changes from baseline to day 7. Some were strongly correlated amongst each other (at baseline the cluster IL-1ß, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, G-CSF, MIP-1α, the cluster PDGF-BB, RANTES or the cluster IL-4, IL-17, Eotaxin, bFGF, TNF-α). The correlation matrix substantially changed from baseline to day 7. The heatmaps of the absolute values of the correlation matrix indicated an association of CCP treatment and clinical outcome with the cytokine pattern. Low levels of IP-10, IFN-γ, MCP-1 and IL-1ß on day 0 were predictive of treatment success in a ROC analysis. In multivariate models, low levels of IL-1ß, IFN-γ and MCP-1 on day 0 were significantly associated with both treatment success and shorter time to clinical improvement. Low levels of IP-10, IL-1RA, IL-6, MCP-1 and IFN-γ on day 7 and high levels of IL-9, PDGF and RANTES on day 7 were predictive of treatment success in ROC analyses. Low levels of IP-10, MCP-1 and high levels of RANTES, on day 7 were associated with both treatment success and shorter time to clinical improvement in multivariate models.
Conclusion: This analysis demonstrates a considerable dynamic of cytokines over time, which is influenced by both treatment and clinical course of COVID-19. Levels of IL-1ß and MCP-1 at baseline and MCP-1, IP-10 and RANTES on day 7 were associated with a favorable outcome across several endpoints. These cytokines should be included in future trials for further evaluation as predictive factors.
Keywords: COVID-19; chemokines; convalescent plasma; interleukins; predictive factors; randomized trial.
Copyright © 2022 Körper, Schrezenmeier, Rincon-Arevalo, Grüner, Zickler, Weiss, Wiesmann, Zacharowski, Kalbhenn, Bentz, Dollinger, Paul, Lepper, Ernst, Wulf, Zinn, Appl, Jahrsdörfer, Rojewski, Lotfi, Dörner, Jungwirth, Seifried, Fürst and Schrezenmeier.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

