Pulsed radiotherapy to mitigate high tumor burden and generate immune memory
- PMID: 36275767
- PMCID: PMC9582356
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.984318
Pulsed radiotherapy to mitigate high tumor burden and generate immune memory
Abstract
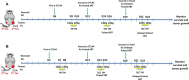
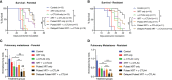
Radiation therapy (XRT) has a well-established role in cancer treatment. Given the encouraging results on immunostimulatory effects, radiation has been increasingly used with immune-check-point inhibitors in metastatic disease, especially when immunotherapy fails due to tumor immune evasion. We hypothesized that using high-dose stereotactic radiation in cycles (pulses) would increase T-cell priming and repertoire with each pulse and build immune memory in an incremental manner. To prove this hypothesis, we studied the combination of anti-CTLA-4 and Pulsed radiation therapy in our 344SQ non-small cell lung adenocarcinoma murine model. Primary and secondary tumors were bilaterally implanted in 129Sv/Ev mice. In the Pulsed XRT group, both primary and secondary tumors received 12Gyx2 radiation one week apart, and blood was collected seven days afterwards for TCR repertoire analysis. As for the delayed-Pulse group, primary tumors received 12Gyx2, and after a window of two weeks, the secondary tumors received 12Gyx2. Blood was collected seven days after the second cycle of radiation. The immunotherapy backbone for both groups was anti-CTLA-4 antibody to help with priming. Treatment with Pulsed XRT + anti-CTLA-4 led to significantly improved survival and resulted in a delayed tumor growth, where we observed enhanced antitumor efficacy at primary tumor sites beyond XRT + anti-CTLA-4 treatment group. More importantly, Pulsed XRT treatment led to increased CD4+ effector memory compared to single-cycle XRT. Pulsed XRT demonstrated superior efficacy to XRT in driving antitumor effects that were largely dependent on CD4+ T cells and partially dependent on CD8+ T cells. These results suggest that combinatorial strategies targeting multiple points of tumor immune evasion may lead to a robust and sustained antitumor response.
Keywords: immune memory; immunotherapy; lung cancer; pulsed radiation; radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2022 Sezen, Barsoumian, He, Hu, Wang, Abana, Puebla-Osorio, Hsu, Wasley, Masrorpour, Wang, Cortez and Welsh.
Conflict of interest statement
JWW reports research support from GlaxoSmithKline, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Merck, Nanobiotix, RefleXion, Alkermes, Artidis, Mavu Pharma, Takeda, Varian, Checkmate Pharmaceuticals and HotSpot Therapeutics. JWW serves/served on the scientific advisory board for Legion Healthcare Partners, RefleXion Medical, MolecularMatch, Merck, AstraZeneca, Aileron Therapeutics, OncoResponse, Checkmate Pharmaceuticals, Mavu Pharma, Alpine Immune Sciences, Ventana Medical Systems, Nanobiotix, China Medical Tribune, GI Innovation, Genentech and Nanorobotix. JWW serves as consultant for Lifescience Dynamics Limited. JWW has/had Speaking Engagements for Ventana Medical Systems, US Oncology, Alkermes, Boehringer Ingelheim, Accuray and RSS. JWW holds/held stock or ownership in Alpine Immune Sciences, Checkmate Pharmaceuticals, Healios, Mavu Pharma, Legion Healthcare Partners, MolecularMatch, Nanorobotix, OncoResponse, and RefleXion. JWW has accepted honoraria in the form of travel costs from Nanobiotix, RefleXion, Varian, Shandong University, The Korea Society of Radiology, Aileron Therapeutics and Ventana. JWW has the following patents: MP470 (amuvatinib), MRX34 regulation of PDL1, XRT technique to overcome immune resistance, Radiotherapies and uses thereof. MD Anderson Cancer Center has a trademark for RadScopal™. HB has the following patent: Radiotherapies and uses thereof. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Anti-glucocorticoid-induced Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Protein (GITR) Therapy Overcomes Radiation-Induced Treg Immunosuppression and Drives Abscopal Effects.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 20;9:2170. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02170. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30294332 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose radiation treatment enhances systemic antitumor immune responses by overcoming the inhibitory stroma.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Oct;8(2):e000537. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000537. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33106386 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic Radiation Therapy Augments Antigen-Specific PD-1-Mediated Antitumor Immune Responses via Cross-Presentation of Tumor Antigen.Cancer Immunol Res. 2015 Apr;3(4):345-55. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0196. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 25527358 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3 agonist enhances radiation-induced immune priming and promotes abscopal responses in anti-PD1 resistant model.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023 Sep;72(9):3003-3012. doi: 10.1007/s00262-023-03471-x. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37289257 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation therapy to enhance tumor immunotherapy: a novel application for an established modality.Int J Radiat Biol. 2019 Jul;95(7):936-939. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2019.1623429. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Int J Radiat Biol. 2019. PMID: 31120369 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic In Situ Cancer Vaccine Using Pulsed Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy-A Translational Model.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Dec 20;12(1):7. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12010007. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38276666 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Rechallenge in the Treatment of Esophageal Squamous Cell Cancer.J Cancer. 2025 Jan 1;16(3):943-951. doi: 10.7150/jca.104380. eCollection 2025. J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39781362 Free PMC article.
-
Novel engineered IL-2 Nemvaleukin alfa combined with PD1 checkpoint blockade enhances the systemic anti-tumor responses of radiation therapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 2;43(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03165-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39218928 Free PMC article.
-
Personalized Ultra-Fractionated Stereotactic Adaptive Radiotherapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Varian Ethos Therapy System.Curr Oncol. 2024 Dec 1;31(12):7625-7630. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31120562. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39727685 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

