Differential retention of adalimumab and etanercept biosimilars compared to originator treatments: Results of a retrospective French multicenter study
- PMID: 36275803
- PMCID: PMC9582272
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.989514
Differential retention of adalimumab and etanercept biosimilars compared to originator treatments: Results of a retrospective French multicenter study
Abstract
Objectives: Previous studies demonstrated equivalence in terms of efficacy and safety of biosimilars (bsDMARDs) compared to original treatments (boDMARDs) and in switching situations. Less is known about what happens when initiating a bsDMARD in a molecule naïve patient. The objectives of our study were to compare the retention of treatment of subcutaneous boDMARDs and bsDMARDs globally, depending on the disease [rheumatoid arthritis (RA), spondyloarthritis (SpA), or psoriatic arthritis (PsA)], molecule [etanercept (ETN) or adalimumab (ADA)], line of treatment, or presence of citrate in the context of first use of each molecule (namely initiation) and to analyze treatment retention's predictive factors.
Materials and methods: This multicenter retrospective study used data from shared medical records of the RIC-FRANCE network, encompassing the prescription of hospital rheumatologists and attached practitioners, of patients with RA, SpA, or PsA, with the starting ETN between 03/10/2016 and 31/07/2020, or ADA between 23/10/2018 and 31/07/2020. Clinical data were collected from medical records. Retention analysis was performed using Kaplan-Meier curves and the log-rank test. Retention's predictive factors were analyzed using Cox proportional-hazard ratio.
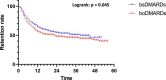
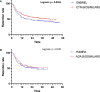
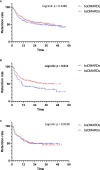
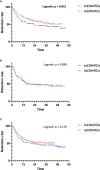
Results: Eight hundred forty-five prescriptions were analyzed: 340 boDMARDs and 505 bsDMARDs. About 57% of prescriptions concerned women. The mean age was 51.8 years. About 38% were prescriptions for RA, 16% for PsA, and 46% for SpA. An increase in the initiation over time was observed for both ETN and ADA. The retention rate of bsDMARDs was superior to boDMARDs' one (39 vs. 23 months; p = 0.045). When molecules are compared, the difference was significant only for ETN (45 vs. 19 months for boDMARD; p = 0.0265). When comparing diseases, the difference in favor of bsDMARDs was significant in patients with RA only (p = 0.041). Citrated treatments displayed better retention compared to citrate-free treatments (p = 0.0137). Multivariable analysis of predictive factors for the cessation of treatment found shorter disease duration, boDMARD prescription, hospital practitioner prescription, late line of treatment, and female sex as significant. More side effects were observed with boDMARDs, especially more infections (17.8% vs. 7.8%).
Conclusion: Even if bsDMARDs' prescription increases over time, its penetration rate is still below expectations. bsDMARDs displayed better retention compared to boDMARDs, especially for ETN, and in patients with RA. Citrated treatments had better retention. Prescription by a full-time hospital-based rheumatologist is associated with poorer retention.
Keywords: TNF-inhibitors; biosimilars; predictive factors; retention rate; survival.
Copyright © 2022 Larid, Baudens, Dandurand, Coquerelle, Goeb, Guyot, Marguerie, Maury, Veillard, Houvenagel, Salmon, Flipo and Gervais.
Conflict of interest statement
GL received support for attending meetings from NOVARTIS, GSK, and AMGEN. VG received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, or educational events from MSD, UCB, Pfizer, Sanofi, Novartis, Abbvie, and Medac. J-HS received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, or educational events from AbbVie, BMS, Galapagos, Janssen, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, UCB, and Viatris. R-MF received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, or educational events from Abbvie, Pfizer, MSD, and Celltrion. EG received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, or educational events from BMS, Sanofi-Aventis, Roche, Abbvie, Novartis, Pfizer, Galapagos, MSD, and Janssen. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Nam JL, Winthrop KL, van Vollenhoven RF, Pavelka K, Valesini G, Hensor EMA, et al. Current evidence for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: a systematic literature review informing the EULAR recommendations for the management of RA. Ann Rheum Dis. (2010) 69:976–86. 10.1136/ard.2009.126573 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Callhoff J, Sieper J, Weiß A, Zink A, Listing J. Efficacy of TNFα blockers in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: a meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2015) 74:1241–8. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Landewé RBM, Bijlsma JWJ, Burmester GR, Dougados M, Kerschbaumer A, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis. (2020) 79:685–99. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216655 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

