Feasibility of a CT-based lymph node radiomics nomogram in detecting lymph node metastasis in PDAC patients
- PMID: 36276058
- PMCID: PMC9579427
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.992906
Feasibility of a CT-based lymph node radiomics nomogram in detecting lymph node metastasis in PDAC patients
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the potential value of a contrast enhanced computed tomography (CECT)-based radiological-radiomics nomogram combining a lymph node (LN) radiomics signature and LNs' radiological features for preoperative detection of LN metastasis in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
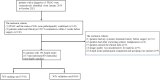
Materials and methods: In this retrospective study, 196 LNs in 61 PDAC patients were enrolled and divided into the training (137 LNs) and validation (59 LNs) cohorts. Radiomic features were extracted from portal venous phase images of LNs. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression algorithm with 10-fold cross-validation was used to select optimal features to determine the radiomics score (Rad-score). The radiological-radiomics nomogram was developed by using significant predictors of LN metastasis by multivariate logistic regression (LR) analysis in the training cohort and validated in the validation cohort independently. Its diagnostic performance was assessed by receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC), decision curve (DCA) and calibration curve analyses.
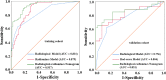
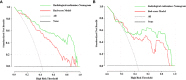
Results: The radiological model, including LN size, and margin and enhancement pattern (three significant predictors), exhibited areas under the curves (AUCs) of 0.831 and 0.756 in the training and validation cohorts, respectively. Nine radiomic features were used to construct a radiomics model, which showed AUCs of 0.879 and 0.804 in the training and validation cohorts, respectively. The radiological-radiomics nomogram, which incorporated the LN Rad-score and the three LNs' radiological features, performed better than the Rad-score and radiological models individually, with AUCs of 0.937 and 0.851 in the training and validation cohorts, respectively. Calibration curve analysis and DCA revealed that the radiological-radiomics nomogram showed satisfactory consistency and the highest net benefit for preoperative diagnosis of LN metastasis.
Conclusions: The CT-based LN radiological-radiomics nomogram may serve as a valid and convenient computer-aided tool for personalized risk assessment of LN metastasis and help clinicians make appropriate clinical decisions for PADC patients.
Keywords: computed tomography; lymph node metastasis; nomogram; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; radiomics.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Song, Zhang, Li, Liu, Yu, Li, Zhang, Ren, Wen and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

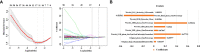

Similar articles
-
Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Based on a Radiomics Nomogram of Dual-Parametric MRI Imaging.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 6;12:927077. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.927077. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35875061 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a CT radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of Ki-67 index in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a two-center retrospective study.Eur Radiol. 2024 May;34(5):2934-2943. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10393-w. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37938382
-
A Radiomics Nomogram for the Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 27;10:1654. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01654. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32974205 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics vs radiologist in bladder and renal cancer. Results from a systematic review.Cent European J Urol. 2023;76(1):12-19. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2023.252. Epub 2023 Jan 21. Cent European J Urol. 2023. PMID: 37064257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Radiomics in the Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Qualitative Assessment Using the Methodological Radiomics Score (METRICS).Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 26;17(5):803. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050803. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075651 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis of resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using dual-layer spectral computed tomography.Eur Radiol. 2025 May;35(5):2692-2701. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-11143-2. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39448418
-
Contrast-enhanced MRI-based intratumoral heterogeneity assessment for predicting lymph node metastasis in resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Insights Imaging. 2025 Mar 30;16(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13244-025-01956-0. Insights Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40159327 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive role of radiomics features extracted from preoperative cross-sectional imaging of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in detecting lymph node metastasis: a systemic review and meta-analysis.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2023 Aug;48(8):2570-2584. doi: 10.1007/s00261-023-03940-y. Epub 2023 May 18. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2023. PMID: 37202642
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

