Delta radiomics model for the prediction of progression-free survival time in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients after immunotherapy
- PMID: 36276082
- PMCID: PMC9583844
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.990608
Delta radiomics model for the prediction of progression-free survival time in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients after immunotherapy
Abstract
Objective: To assess the validity of pre- and posttreatment computed tomography (CT)-based radiomics signatures and delta radiomics signatures for predicting progression-free survival (PFS) in stage III-IV non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients after immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy.
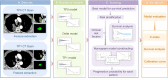
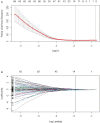
Methods: Quantitative image features of the largest primary lung tumours were extracted on CT-enhanced imaging at baseline (time point 0, TP0) and after the 2nd-3rd immunotherapy cycles (time point 1, TP1). The critical features were selected to construct TP0, TP1 and delta radiomics signatures for the risk stratification of patient survival after ICI treatment. In addition, a prediction model integrating the clinicopathologic risk characteristics and phenotypic signature was developed for the prediction of PFS.
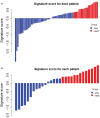
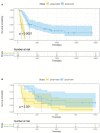
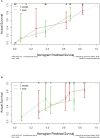
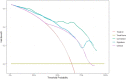
Results: The C-index of TP0, TP1 and delta radiomics models in the training and validation cohort were 0.64, 0.75, 0.80, and 0.61, 0.68, 0.78, respectively. The delta radiomics score exhibited good accuracy for distinguishing patients with slow and rapid progression to ICI treatment. The predictive accuracy of the combined prediction model was higher than that of the clinical prediction model in both training and validation sets (P<0.05), with a C-index of 0.83 and 0.70, respectively. Additionally, the delta radiomics model (C-index of 0.86) had a higher predictive accuracy compared to PD-L1 expression (C-index of 0.50) (P<0.0001).
Conclusions: The combined prediction model including clinicopathologic characteristics (tumour anatomical classification and brain metastasis) and the delta radiomics signature could achieve the individualized prediction of PFS in ICIs-treated NSCLC patients.
Keywords: delta; immunity; non-small-cell lung cancer; prediction model; radiomics.
Copyright © 2022 Xie, Xu, Zhu, Pu, Huang, Lou, Wu, Huang, He and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Predictive value of delta-radiomic features for prognosis of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 30;13(6):1247-1263. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-7. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38973966 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the immune therapy response of advanced non-small cell lung cancer based on primary tumor and lymph node radiomics features.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 3;12:1541376. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1541376. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40248083 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Microwave Ablation Early Efficacy in Pulmonary Malignancies via Δ Radiomics Models.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2024 Sep-Oct 01;48(5):794-802. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000001611. Epub 2024 Apr 24. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2024. PMID: 38657155
-
Progress in Serial Imaging for Prognostic Stratification of Lung Cancer Patients Receiving Immunotherapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 31;16(3):615. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030615. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delta-radiomics-based models for toxicity prediction in radiotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2023 Aug;67(5):564-579. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.13546. Epub 2023 Jun 13. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37309680
Cited by
-
MRI-based intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics for preoperative prediction of glioma grade: a multicenter study.Front Oncol. 2024 May 13;14:1401977. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1401977. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38803534 Free PMC article.
-
Delta radiomics: an updated systematic review.Radiol Med. 2024 Aug;129(8):1197-1214. doi: 10.1007/s11547-024-01853-4. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Radiol Med. 2024. PMID: 39017760 Free PMC article.
-
Gender Medicine in Clinical Radiology Practice.J Pers Med. 2023 Jan 27;13(2):223. doi: 10.3390/jpm13020223. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36836457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical applications of radiomics in non-small cell lung cancer patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 20;14:1251645. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1251645. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37799725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiomics nomogram for the prediction of Ki-67 index in advanced non-small cell lung cancer based on dual-phase enhanced computed tomography.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep;149(11):9301-9315. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04856-2. Epub 2023 May 19. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37204513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, Felip E, Perez-Gracia JL, Han JY, et al. . Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet (2016) 387(10027):1540–50. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01281-7 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

