[Jaundice in Young Children]
- PMID: 36276206
- PMCID: PMC9574292
- DOI: 10.3348/jksr.2022.0091
[Jaundice in Young Children]
Abstract
Jaundice in children have various etiologies. Among them, physiological jaundice is a very common disease observed in more than half of full-term neonates. When jaundice persists or develops after 2 weeks of age, the total/direct bilirubin is measured in consideration of the possibility of cholestasis. In case of cholestasis, imaging studies differentiate biliary atresia and other disorders of the extrahepatic bile ducts. In this review, we briefly presented the major differential diseases of cholestasis in children and introduced diagnostic imaging techniques, including normal findings.
신생아와 유소아 황달은 다양한 원인에 의하여 발생하며, 특히 생리적 황달의 경우는 만삭아의 반수 이상에서 관찰되는 매우 흔한 질환이다. 생후 2주 이후 황달이 지속되거나 새로이 발생하는 경우, 담즙 정체의 가능성을 고려하여 총/직접 빌리루빈을 측정하게 되며, 담즙 정체로 판단되는 경우 외과적 치료를 요하는 간외 담도 폐쇄 질환을 감별하려는 목적으로 영상 검사가 의뢰된다. 본 종설에서는 신생아 및 유소아에서 황달을 발생시킬 수 있는 질환들을 분류하고, 질환들을 진단하기 위한 여러 영상 검사들의 종류와 방법 및 정상 소견들을 기술하며, 연령별로 흔히 발생하는 각 질환에 대한 영상 소견들을 소개하고자 한다.
Copyrights © 2022 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

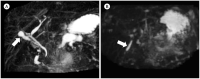
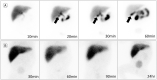
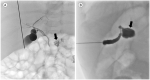

References
-
- Ko JS, Seo JK. The etiologies of neonatal cholestasis. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50:835–840.
-
- Anderson NB, Calkins KL. Neonatal indirect hyperbilirubinemia. Neoreviews. 2020;21:e749–e760. - PubMed
-
- Choe BH. Early exclusive diagnosis of biliary atresia among infants with cholestasis. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011;14:122–129.
-
- Gubernick JA, Rosenberg HK, Ilaslan H, Kessler A. US approach to jaundice in infants and children. Radiographics. 2000;20:173–195. - PubMed
-
- Cho HH, Kim WS, Choi YH, Cheon JE, Lee SM, Kim IO, et al. Ultrasonography evaluation of infants with Alagille syndrome: in comparison with biliary atresia and neonatal hepatitis. Eur J Radiol. 2016;85:1045–1052. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

