The impact of medication on osseointegration and implant anchorage in bone determined using removal torque-A review
- PMID: 36276721
- PMCID: PMC9582727
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10844
The impact of medication on osseointegration and implant anchorage in bone determined using removal torque-A review
Abstract
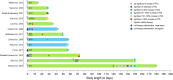
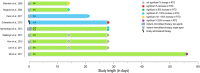
Permanently anchored metal implants are frequently used in dental, craniomaxillofacial, and orthopaedic rehabilitation. The success of such therapies is owed to the phenomenon of osseointegration-the direct connection between the living bone and the implant. The extent of biomechanical anchorage (i.e., physical interlocking between the implant and bone) can be assessed with removal torque (RTQ) measurement. Implant anchorage is strongly influenced by underlying bone quality, involving physicochemical and biological properties such as composition and structural organisation of extracellular matrix, extent of micro-damage, and bone turnover. In this review, we evaluated the impact of various pharmacological agents on osseointegration, from animal experiments conducting RTQ measurements. In addition to substances whose antiresorptive and/or anti-catabolic effects on bone are well-documented (e.g., alendronate, zoledronate, ibandronate, raloxifene, human parathyroid hormone, odanacatib, and the sclerostin monoclonal antibody), positive effects on RTQ have been reported for substances that do not primarily target bone (e.g., aminoguanidine, insulin, losartan, simvastatin, bone morphogenetic protein, alpha-tocopherol, and the combination of silk fibroin powder and platelet-rich fibrin). On the contrary, several substances (e.g., prednisolone, cyclosporin A, cisplatin, and enamel matrix derivative) tend to adversely impact RTQ. While morphometric parameters such as bone-implant contact appear to influence the biomechanical anchorage, increased or decreased RTQ is not always accompanied by corresponding fluctuations in bone-implant contact. This further confirms that factors such as bone quality underpin biomechanical anchorage of metal implants. Several fundamental questions on drug metabolism and bioavailability, drug dosage, animal-to-human translation, and the consequences of treatment interruption remain yet unanswered.
Keywords: Bisphosphonates; Bone; Drug delivery; Implant; In vivo; Osseointegration; Removal torque.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Laser-Modified Surface Enhances Osseointegration and Biomechanical Anchorage of Commercially Pure Titanium Implants for Bone-Anchored Hearing Systems.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 14;11(6):e0157504. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157504. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27299883 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of different surface modifications for titanium implants installed into the goat iliac crest.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016 Feb;27(2):e57-67. doi: 10.1111/clr.12529. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016. PMID: 25486997
-
The effects of controlled nanotopography, machined topography and their combination on molecular activities, bone formation and biomechanical stability during osseointegration.Acta Biomater. 2021 Dec;136:279-290. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.10.001. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 34626821
-
Adjuvant therapies of bone graft around non-cemented experimental orthopedic implants stereological methods and experiments in dogs.Acta Orthop Suppl. 2008 Aug;79(330):1-43. Acta Orthop Suppl. 2008. PMID: 19065776 Review.
-
Comparison of the Use of Titanium-Zirconium Alloy and Titanium Alloy in Dental Implants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Oral Implantol. 2018 Aug;44(4):305-312. doi: 10.1563/aaid-joi-D-17-00233. Epub 2018 Feb 19. J Oral Implantol. 2018. PMID: 29457740
Cited by
-
Comparing the stability of implants coated with nano PLGA-alendronate sodium: an in-vivo study.Biomater Investig Dent. 2025 Mar 31;12:43372. doi: 10.2340/biid.v12.43372. eCollection 2025. Biomater Investig Dent. 2025. PMID: 40191582 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin receptor gene deficiency minimally affects osseointegration in rats.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 20;13(1):15631. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42379-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37730735 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of Chronic Stress and Hypertension with Bone Resorption.J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2025 Jan 4;10(1):21. doi: 10.3390/jfmk10010021. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2025. PMID: 39846662 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abtahi J., Agholme F., Sandberg O., Aspenberg P. Bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis of the jaw in a rat model arises first after the bone has become exposed. No primary necrosis in unexposed bone. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2012;41:494–499. - PubMed
-
- Abtahi J., Agholme F., Sandberg O., Aspenberg P. Effect of local vs. systemic bisphosphonate delivery on dental implant fixation in a model of osteonecrosis of the jaw. J. Dent. Res. 2013;92:279–283. - PubMed
-
- Adell R., Lekholm U., Rockler B., Brånemark P.I. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int. J. Oral Surg. 1981;10:387–416. - PubMed
-
- Aerssens J., Boonen S., Lowet G., Dequeker J. Interspecies differences in bone composition, density, and quality: potential implications for in vivo bone research. Endocrinology. 1998;139:663–670. - PubMed
-
- Albrektsson T., Brånemark P.I., Hansson H.A., Lindström J. Osseointegrated titanium implants. Requirements for ensuring a long-lasting, direct bone-to-implant anchorage in man. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1981;52:155–170. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

