Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Glioma Brain Tumor Detection and Classification Using Convolutional Neural Network
- PMID: 36277002
- PMCID: PMC9586767
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4380901
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Glioma Brain Tumor Detection and Classification Using Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
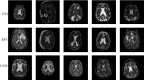
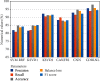
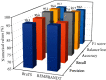
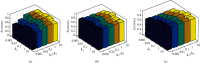
The classification of the brain tumor image is playing a vital role in the medical image domain, and it directly assists the clinicians to understand the severity and to take an appropriate solution. The magnetic resonance imaging tool is used to analyze the brain tissues and to examine the different portion of brain circumstance. We propose the convolutional neural network database learning along with neighboring network limitation (CDBLNL) technique for brain tumor image classification in medical image processing domain. The proposed system architecture is constructed with multilayer-based metadata learning, and they have integrated with CNN layer to deliver the accurate information. The metadata-based vector encoding is used, and the type of coding estimation for extra dimension is known as sparse. In order to maintain the supervised data in terms of geometric format, the atoms of neighboring limitation are built based on a well-structured k-neighbored network. The resultant of the proposed system is considerably strong and subjective for classification. The proposed system used two different datasets, such as BRATS and REMBRANDT, and the proposed brain MRI classification technique outcome is more efficient than the other existing techniques.
Copyright © 2022 S. Saravanan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Rajendran S., Mathivanan S. K., Jayagopal P., et al. Emphasizing privacy and security of edge intelligence with machine learning for healthcare. International Journal of Intelligent Computing and Cybernetics . 2022;15(1):92–109. doi: 10.1108/IJICC-05-2021-0099. - DOI
-
- Balasooriya N. M., Nawarathna R. D. A sophisticated convolutional neural network model for brain tumor classification. 2017 IEEE international conference on industrial and information systems; 2017; Peradeniya, Sri Lanka. pp. 1–5. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

