Gamification for Distal Radius Fracture Rehabilitation: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study
- PMID: 36277562
- PMCID: PMC9580983
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.29333
Gamification for Distal Radius Fracture Rehabilitation: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study
Abstract
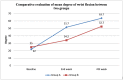
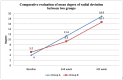
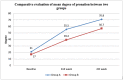
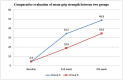
Introduction Gamification is a novel interventional approach to functional recovery and rehabilitation. A significant impact has been observed with the application of gamification on non-traumatic conditions and chronic neurological and musculoskeletal illnesses; however, the implication of gamification on the functional recovery of patients with distal radius fractures (DRF) is yet to be explored. Methodology This pilot study included 20 post-DRF patients aged 18-65 years with unilateral DRF, managed with closed reduction and K-wire internal fixation. The patients were assigned to group A (gamification) and group B (conventional rehabilitation) in a 1:1 ratio. Group A patients played Racket: NX game, Until you fall game, and Holofit game on Oculus Quest head-mounted display (HMD) (Oculus, USA), while group B patients received a conventional rehabilitation program. Both groups underwent a rehabilitation program for 60 min/day, five days a week, for four weeks. The visual analogue scale (VAS), universal goniometer, Jamar dynamometer, and Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) questionnaire were used as outcome measures at baseline, at the end of the second week, and at the end of treatment. Results There were significant improvements in pain, range of motion (ROM), grip strength, and functional independence in both groups. However, improvements in hand function and functional independence were significantly greater in the gamification group than in the conventional physiotherapy rehabilitation group. Conclusion The study concluded that gamification appears to have a significant impact on post-DRF rehabilitation in terms of pain, ROM, grip strength, and functional independence. Further research with larger sample sizes is required to confirm the preliminary findings.
Keywords: distal radial fracture; functional independence; gamification; grip strength; oculus quest; pain; physiotherapy; pilot study; virtual reality.
Copyright © 2022, Naqvi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gamification in Therapeutic Rehabilitation of Distal Radial and Ulnar Fracture: A Case Report.Cureus. 2022 Aug 30;14(8):e28586. doi: 10.7759/cureus.28586. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36185862 Free PMC article.
-
A research protocol on leap motion tracking device: A novel intervention method in distal radial fracture rehabilitation.PLoS One. 2022 May 6;17(5):e0267549. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267549. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35522618 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Synthesis of the Literature on the Evolution of Gamification in Distal Radial Fracture Rehabilitation.Cureus. 2022 Sep 20;14(9):e29382. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29382. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36304351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A multicenter randomized controlled trial comparing gamification with remote monitoring against standard rehabilitation for patients after arthroscopic shoulder surgery.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022 Jan;31(1):8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2021.08.019. Epub 2021 Sep 26. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022. PMID: 34587534 Clinical Trial.
-
In adults, early mobilization may be beneficial for distal radius fractures treated with open reduction and internal fixation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Nov 24;16(1):691. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02837-0. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34819123 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Areas of Research Focus and Trends in the Research on the Application of VR in Rehabilitation Medicine.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jul 18;11(14):2056. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11142056. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510497 Free PMC article.
-
Rehabilitation after Distal Radius Fractures: Opportunities for Improvement.J Wrist Surg. 2023 Jul 5;12(5):460-473. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1769925. eCollection 2023 Oct. J Wrist Surg. 2023. PMID: 37841352 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Virtual Reality for Pain Management in Musculoskeletal Disorders Across Anatomical Regions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Musculoskeletal Care. 2025 Mar;23(1):e70041. doi: 10.1002/msc.70041. Musculoskeletal Care. 2025. PMID: 39754331 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Applications of Virtual Reality in Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Dec 15;11(24):3178. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11243178. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- A systematic review of gamification in e-Health. Sardi L, Idri A, Fernández-Alemán JL. J Biomed Inform. 2017;71:31–48. - PubMed
-
- Virtual reality in the treatment of adults with chronic low back pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Brea-Gómez B, Torres-Sánchez I, Ortiz-Rubio A, Calvache-Mateo A, Cabrera-Martos I, López-López L, Valenza MC. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18 - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
