Relationship between Dynamic Changes of Microcirculation Flow, Tissue Perfusion Parameters, and Lactate Level and Mortality of Septic Shock in ICU
- PMID: 36277595
- PMCID: PMC9568350
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1192902
Relationship between Dynamic Changes of Microcirculation Flow, Tissue Perfusion Parameters, and Lactate Level and Mortality of Septic Shock in ICU
Abstract
Background: Septic shock is a common clinical critical disease with high mortality, hemodynamic instability, and easy to be complicated with multiple organ failure. The rapid progress of the patient's condition poses a serious threat to patient's safety.
Aim: To investigate the relationship between the dynamic monitoring of microcirculation perfusion parameters and blood lactic acid level and the prognosis of patients with infection shock in ICU.
Methods: A total of 104 patients with septic shock admitted to ICU of Affiliated Hai'an Hospital of Nantong University from February 2018 to June 2021 were selected for clinical research. According to the survival situation of patients after 28 days of treatment, they were divided into the death group (n = 48) and the survival group (n = 56). The central venous-arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure difference (Pcv-aCO2), the ratio of central venous-arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure difference to arterial central venous oxygen content difference (Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2), and blood lactic acid level were retrospectively analyzed and compared between the two groups on the first, third, and seventh days after admission to ICU. The odds ratio (OR) of three indexes affecting the prognosis of patients with septic shock was analyzed by univariate and multivariate mathematical models, and the value of three indexes in predicting the prognosis of patients was analyzed by receiver operating curve (ROC).
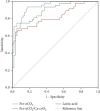
Results: Pcv-aCO2 and lactic acid in the death group were higher than those in the survival group on the 1st, 3rd, and 7th day of ICU stay (P < 0.05). The Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 of the death group was higher than that of the survival group on the 3rd and 7th day of ICU stay (P < 0.05). Logistic model results showed that age, SOFA score, APACHE II score, the number of multiple organ failure (MODS), intracranial infection, the increase of Pcv-aCO2, Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2, and the increase of lactic acid were independent risk factors for death in patients with septic shock (OR values were 1.519, 1.808, 1.781, 1.912, 2.069, 1.848, 1.781, and 1.642, respectively, P < 0.05). The results showed that the AUC value of Pcv-aCO2 in predicting death was 0.943, and the sensitivity and specificity were 93.72% and 83.09%, respectively. The AUC value of Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 for predicting death was 0.887, and the sensitivity and specificity were 81.63% and 77.56%, respectively. The AUC value of lactic acid in predicting death of patients was 0.825, and the sensitivity and specificity were 71.66% and 82.09%, respectively.
Conclusion: Changes of microcirculation flow tissue perfusion parameters and blood lactic acid level changes are closely related to the prognosis of patients with septic shock, which is of great value in the evaluation of the prognosis of patients with septic shock.
Copyright © 2022 Xuebing Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest regarding this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Venous Minus Arterial Carbon Dioxide Gradients in the Monitoring of Tissue Perfusion and Oxygenation: A Narrative Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Jul 6;59(7):1262. doi: 10.3390/medicina59071262. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37512072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Prognostic value of arterial lactate combined with central venous-to-arterial carbon dioxide difference to arterial-to-central venous oxygen content difference ratio in septic shock patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Jan;32(1):39-43. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20191226-00007. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32148229 Chinese.
-
Pcv-aCO2/Ca-cvO2 Combined With Arterial Lactate Clearance Rate as Early Resuscitation Goals in Septic Shock.Am J Med Sci. 2019 Sep;358(3):182-190. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2019.04.025. Epub 2019 May 6. Am J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31229247
-
[Prognostic value of difference between peripheral venous and arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide in patients with septic shock: a pilot study].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2018 Nov 30;38(11):1312-1317. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2018.11.06. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2018. PMID: 30514678 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Comparison of central venous minus arterial carbon dioxide pressure to arterial minus central venous oxygen content ratio and lactate levels as predictors of mortality in critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022 Apr-Jun;34(2):279-286. doi: 10.5935/0103-507X.20220026-pt. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2022. PMID: 35946659 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The lactate to albumin ratio linked to all-cause mortality in critically ill patients with septic myocardial injury.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Sep 13;10:1233147. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1233147. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37790597 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes and prognosis of postpartum hemorrhage according to management protocol: an 11-year retrospective study from two referral centers.World J Emerg Surg. 2024 Aug 1;19(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13017-024-00556-5. World J Emerg Surg. 2024. PMID: 39090705 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of Multiple Acute Concomitant Cerebral Infarcts Involving Different Arterial Territories.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 11;12(12):3973. doi: 10.3390/jcm12123973. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37373666 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between lactate/albumin ratio and 28-day mortality in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury patients.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 5;12:1546112. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1546112. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40538408 Free PMC article.
-
Venous Minus Arterial Carbon Dioxide Gradients in the Monitoring of Tissue Perfusion and Oxygenation: A Narrative Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Jul 6;59(7):1262. doi: 10.3390/medicina59071262. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37512072 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang W., Yang Y. P., Tasneem S., et al. Lanostane tetracyclic triterpenoids as important sources for anti-inflammatory drug discovery. World J Tradit Chin Med . 2020;6(3):229–238. doi: 10.4103/wjtcm.wjtcm_17_20. - DOI
-
- Jeremy W., Michael K., Chanu R. What Is the utility of measuring lactate levels in patients with sepsis and septic shock? Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine . 2021;42(5):650–661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources