EEG-based emotion recognition using hybrid CNN and LSTM classification
- PMID: 36277613
- PMCID: PMC9585893
- DOI: 10.3389/fncom.2022.1019776
EEG-based emotion recognition using hybrid CNN and LSTM classification
Abstract
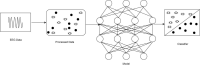
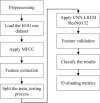
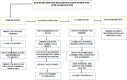
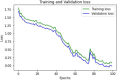
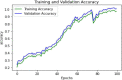
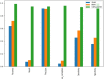
Emotions are a mental state that is accompanied by a distinct physiologic rhythm, as well as physical, behavioral, and mental changes. In the latest days, physiological activity has been used to study emotional reactions. This study describes the electroencephalography (EEG) signals, the brain wave pattern, and emotion analysis all of these are interrelated and based on the consequences of human behavior and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Post-traumatic stress disorder effects for long-term illness are associated with considerable suffering, impairment, and social/emotional impairment. PTSD is connected to subcortical responses to injury memories, thoughts, and emotions and alterations in brain circuitry. Predominantly EEG signals are the way of examining the electrical potential of the human feelings cum expression for every changing phenomenon that the individual faces. When going through literature there are some lacunae while analyzing emotions. There exist some reliability issues and also masking of real emotional behavior by the victims. Keeping this research gap and hindrance faced by the previous researchers the present study aims to fulfill the requirements, the efforts can be made to overcome this problem, and the proposed automated CNN-LSTM with ResNet-152 algorithm. Compared with the existing techniques, the proposed techniques achieved a higher level of accuracy of 98% by applying the hybrid deep learning algorithm.
Keywords: deep learning; electroencephalography; emotion recognition; machine learning; neural networks.
Copyright © 2022 Chakravarthi, Ng, Ezilarasan and Leung.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Automated accurate emotion recognition system using rhythm-specific deep convolutional neural network technique with multi-channel EEG signals.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Jul;134:104428. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104428. Epub 2021 May 6. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33984749
-
An Investigation of Deep Learning Models for EEG-Based Emotion Recognition.Front Neurosci. 2020 Dec 23;14:622759. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.622759. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33424547 Free PMC article.
-
A transfer learning-based CNN and LSTM hybrid deep learning model to classify motor imagery EEG signals.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Apr;143:105288. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105288. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35168083
-
Fused CNN-LSTM deep learning emotion recognition model using electroencephalography signals.Int J Neurosci. 2023 Jun;133(6):587-597. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2021.1941947. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Int J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 34121598
-
Emotion recognition in EEG signals using deep learning methods: A review.Comput Biol Med. 2023 Oct;165:107450. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107450. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37708717 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding of facial features in face perception: insights from deep convolutional neural networks.Front Comput Neurosci. 2024 Apr 9;18:1209082. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2024.1209082. eCollection 2024. Front Comput Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38655070 Free PMC article.
-
Emotion Recognition Using EEG Signals and Audiovisual Features with Contrastive Learning.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Oct 3;11(10):997. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11100997. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451373 Free PMC article.
-
Latent Prototype-Based Clustering: A Novel Exploratory Electroencephalography Analysis Approach.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 29;24(15):4920. doi: 10.3390/s24154920. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123966 Free PMC article.
-
A BERT Framework to Sentiment Analysis of Tweets.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 2;23(1):506. doi: 10.3390/s23010506. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36617101 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Neural Correlates of Flow Experience with Multifaceted Tasks and a Single-Channel Prefrontal EEG Recording.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Mar 15;24(6):1894. doi: 10.3390/s24061894. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38544157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen K., Che H., Li X., Leung M. F. (2022). Graph non-negative matrix factorization with alternative smoothed $$L_0$$ regularizations. Neural Comput. Appl. 1–15. 10.1007/s00521-022-07200-w - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

