Calcium scoring in low-dose ungated chest CT scans using convolutional long-short term memory networks
- PMID: 36277935
- PMCID: PMC9585987
- DOI: 10.1117/12.2613147
Calcium scoring in low-dose ungated chest CT scans using convolutional long-short term memory networks
Abstract
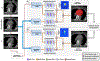
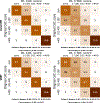
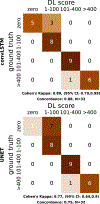
We aimed to develop a novel deep-learning based method for automatic coronary artery calcium (CAC) quantification in low-dose ungated computed tomography attenuation correction maps (CTAC). In this study, we used convolutional long-short -term memory deep neural network (conv-LSTM) to automatically derive coronary artery calcium score (CAC) from both standard CAC scans and low-dose ungated scans (CT-attenuation correction maps). We trained convLSTM to segment CAC using 9543 scans. A U-Net model was trained as a reference method. Both models were validated in the OrCaCs dataset (n=32) and in the held-out cohort (n=507) without prior coronary interventions who had CTAC standard CAC scan acquired contemporarily. Cohen's kappa coefficients and concordance matrices were used to assess agreement in four CAC score categories (very low: <10, low:10-100; moderate:101-400 and high >400). The median time to derive results on a central processing unit (CPU) was significantly shorter for the conv-LSTM model- 6.18s (inter quartile range [IQR]: 5.99, 6.3) than for UNet (10.1s, IQR: 9.82, 15.9s, p<0.0001). The memory consumption during training was much lower for our model (13.11Gb) in comparison with UNet (22.31 Gb). Conv-LSTM performed comparably to UNet in terms of agreement with expert annotations, but with significantly shorter inference times and lower memory consumption.
Keywords: Convolutional LSTM; Coronary calcium scoring; PET CTAC; deep learning.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deep Learning Coronary Artery Calcium Scores from SPECT/CT Attenuation Maps Improve Prediction of Major Adverse Cardiac Events.J Nucl Med. 2023 Apr;64(4):652-658. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.122.264423. Epub 2022 Oct 7. J Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 36207138 Free PMC article.
-
Reproducibility of quantitative coronary calcium scoring from PET/CT attenuation maps: comparison to ECG-gated CT scans.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022 Oct;49(12):4122-4132. doi: 10.1007/s00259-022-05866-x. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35751666 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning of Coronary Calcium Scores From PET/CT Attenuation Maps Accurately Predicts Adverse Cardiovascular Events.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023 May;16(5):675-687. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2022.06.006. Epub 2022 Sep 14. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36284402
-
Automatic determination of cardiovascular risk by CT attenuation correction maps in Rb-82 PET/CT.J Nucl Cardiol. 2018 Dec;25(6):2133-2142. doi: 10.1007/s12350-017-0866-3. Epub 2017 Apr 4. J Nucl Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 28378112 Free PMC article.
-
Scoring of coronary artery calcium scans: history, assumptions, current limitations, and future directions.Atherosclerosis. 2015 Mar;239(1):109-17. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.12.040. Epub 2015 Jan 2. Atherosclerosis. 2015. PMID: 25585030 Review.
Cited by
-
Automated proximal coronary artery calcium identification using artificial intelligence: advancing cardiovascular risk assessment.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2025 Mar 3;26(3):471-480. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeaf007. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39821011
-
Deep Learning Coronary Artery Calcium Scores from SPECT/CT Attenuation Maps Improve Prediction of Major Adverse Cardiac Events.J Nucl Med. 2023 Apr;64(4):652-658. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.122.264423. Epub 2022 Oct 7. J Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 36207138 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting mortality from AI cardiac volumes mass and coronary calcium on chest computed tomography.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 29;15(1):2747. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46977-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38553462 Free PMC article.
-
Automated vessel-specific coronary artery calcification quantification with deep learning in a large multi-centre registry.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024 Jun 28;25(7):976-985. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeae045. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38376471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dilsizian V, Bacharach SL, Beanlands RS, Bergmann SR, Delbeke D, Dorbala S, et al. ASNC imaging guidelines/SNMMI procedure standard for positron emission tomography (PET) nuclear cardiology procedures 2016. - PubMed
-
- Mylonas I, Kazmi M, Fuller L, De Kemp RA, Yam Y, Chen L, et al. Measuring coronary artery calcification using positron emission tomography-computed tomography attenuation correction images. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2012;13(9):786–92. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
