The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Childhood Obesity and Lifestyle-A Report from Italy
- PMID: 36278553
- PMCID: PMC9589932
- DOI: 10.3390/pediatric14040049
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Childhood Obesity and Lifestyle-A Report from Italy
Abstract
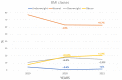
During the COVID-19 lockdown, especially in the first wave of pandemic (March 2020), sedentary lifestyle and calorie intake increase in children became considerably more prevalent. The aim of the present paper was to evaluate changes in children's weights and nutritional habits during the COVID-19 pandemic in Italy. In this cross-sectional observational study, for 3 years, as part of the corporate wellness program (2019-2021) in Emilia Romagna region of Italy, anthropometric data of Ferrari car company employers' children were collected, analyzed, and compared. Moreover, at the visit of November 2020, performed after the first wave of the pandemic with the most rigorous lockdown rules in Italy, a questionnaire on nutritional and lifestyle habits was administered. We evaluated 307 children (163 M, 10.1 ± 2.3 mean aged in 2019). A significant increase in BMI percentile in 2020 (65.2) compared to 2019 (49.2) was observed; it was confirmed, albeit slightly decreased, in 2021 (64.5). About one-third of participants reported an increase in consumption of fatty condiments and more than half report an increase in consumption of junk food. Levels of physical activity were still high during the COVID-19 lockdown, while sleeping time was significantly reduced. Our findings alert us to the importance of carefully monitoring eating behaviors in young to avoid the adoption of unhealthy food habits and prevent childhood obesity, especially during the period of COVID-19 lockdown.
Keywords: COVID-19 lockdown; childhood obesity; eating habits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wijnhoven T., van Raaij J., Spinelli A., Starc G., Hassapidou M., Spiroski I., Rutter H., Martos É., Rito A.I., Hovengen R., et al. WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative: Body mass index and level of overweight among 6–9-year-old children from school year 2007/2008 to school year 2009/2010. BMC Public Health. 2014;14:806. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-806. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fact sheet—Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative (COSI): Physical Activity, Screen Time and Sleep of Children Aged 6–9 in Europe. 2020. [(accessed on 23 August 2022)]. Available online: https://childhoodobesity.ie/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/COSI-WHO-2020-Fac....
-
- WHO: Obesity and Overweight. [(accessed on 23 August 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
-
- Compagno S., Palermi S., Pescatore V., Brugin E., Sarto M., Marin R., Calzavara V., Nizzetto M., Scevola M., Aloi A., et al. Physical and psychological reconditioning in long COVID syndrome: Results of an out-of-hospital exercise and psychological-based rehabilitation program. Int. J. Cardiology. Heart Vasc. 2022;41:101080. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2022.101080. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources