Discovery of N-quinazolinone-4-hydroxy-2-quinolone-3-carboxamides as DNA gyrase B-targeted antibacterial agents
- PMID: 36278813
- PMCID: PMC9186351
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2084088
Discovery of N-quinazolinone-4-hydroxy-2-quinolone-3-carboxamides as DNA gyrase B-targeted antibacterial agents
Abstract
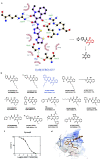
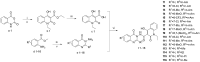
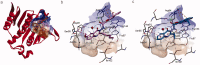
Emerging drug resistance is generating an urgent need for novel and effective antibiotics. A promising target that has not yet been addressed by approved antibiotics is the bacterial DNA gyrase subunit B (GyrB), and GyrB inhibitors could be effective against drug-resistant bacteria, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). Here, we used the 4-hydroxy-2-quinolone fragment to search the Specs database of purchasable compounds for potential inhibitors of GyrB and identified AG-690/11765367, or f1, as a novel and potent inhibitor of the target protein (IC50: 1.21 µM). Structural modification was used to further identify two more potent GyrB inhibitors: f4 (IC50: 0.31 µM) and f14 (IC50: 0.28 µM). Additional experiments indicated that compound f1 is more potent than the others in terms of antibacterial activity against MRSA (MICs: 4-8 µg/mL), non-toxic to HUVEC and HepG2 (CC50: approximately 50 µM), and metabolically stable (t1/2: > 372.8 min for plasma; 24.5 min for liver microsomes). In summary, this study showed that the discovered N-quinazolinone-4-hydroxy-2-quinolone-3-carboxamides are novel GyrB-targeted antibacterial agents; compound f1 is promising for further development.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance; DNA Gyrase inhibitors; MRSA; antibacterial agent; computer-aided drug design.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
Figures
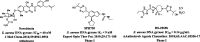
References
-
- O’Neill J. Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: final report and recommendations. UK: Wellcome Trust and HM Government; 2016.
-
- Rice LB. Federal funding for the study of antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial pathogens: no ESKAPE. J Infect Dis 2008;197:1620–81. - PubMed
-
- Bassetti M, Russo A, Carnelutti A, et al. . Emerging drugs for treating methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 2019;24:191–204. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
