Centella asiatica extract-SiO2 nanocomposite: More than a drug-delivery system for skin protection from oxidative damage
- PMID: 36278820
- PMCID: PMC10092495
- DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.37462
Centella asiatica extract-SiO2 nanocomposite: More than a drug-delivery system for skin protection from oxidative damage
Abstract
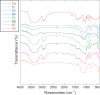
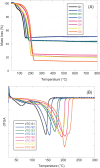
An innovative nanotechnology-based approach was used for the preparation of Centella asiatica (C. asiatica) extract-SiO2 nanocomposites, specifically tailored for skin protection from oxidative damage. Different amounts of C. asiatica glycolic extract (1.0, 3.0, 5.0, and 10.0 wt %) and fumed silica were used to prepare the nanocomposites by means of ball milling method. The influence of both composition of the starting mixture and milling time on the final products was evaluated by different techniques such as X-ray powder diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, and nitrogen sorption analysis. Results confirmed the integrity of the natural extract after the milling process, and its successful loading in the silica matrix. No cytotoxicity was observed for the obtained nanocomposites, which showed high in-vitro ability to scavenge 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl and to protect human keratinocytes from damages induced with hydrogen peroxide.
Keywords: Centella asiatica; antioxidant activity; ball milling; biomaterial; fumed silica; nanocomposites; oxidative damage; skin protection.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures






References
-
- Paocharoen V. The efficacy and side effects of oral Centella asiatica extract for wound healing promotion in diabetic wound patients. J Med Assoc Thai. 2010;93(Suppl 7):S166‐S170. - PubMed
-
- Liu M, Dai Y, Li Y, et al. Madecassoside isolated from Centella asiatica herbs facilitates burn wound healing in mice. Planta Med. 2008;74(8):809‐815. - PubMed
-
- Shetty BS, Udupa SL, Udupa AL, Somayaji SN. Effect of Centella asiatica L (Umbelliferae) on Normal and dexamethasone‐suppressed wound healing in Wistar albino rats. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2006;5:137‐143. - PubMed
-
- Shukla A, Rasik AM, Jain GK, Shankar R, Kulshrestha DK, Dhawan BN. In vitro and in vivo wound healing activity of asiaticoside isolated from Centella asiatica. J Ethnopharmacol. 1999;65:1‐11. - PubMed
-
- Maquart FX, Chastang F, Simeon A, Birembaut P, Gillery P, Wegrowski Y. Triterpenes from Centella asiatica stimulate extracellular matrix accumulation in rat experimental wounds. Eur J Dermatol. 1999;9:289‐296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

