Platinum-based adjuvant therapy was efficient for triple-negative breast cancer: a meta-analysis from randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 36278891
- PMCID: PMC9601551
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2115616
Platinum-based adjuvant therapy was efficient for triple-negative breast cancer: a meta-analysis from randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most aggressive breast cancer. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy was widely accepted for treating TNBC. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and survival benefit of platinum-based adjuvant therapy (PBAT) in treating TNBC. The keywords were searched in Medline, Embase, Pubmed, and Cochrane Library database up to July 24, 2022. All the randomized control trials (RCTs) comparing PBAT and non-PBAT in treating TNBC were included in our study. The pathological complete remission (pCR) and complications were compared by odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The overall survival (OS) and relapse-free survival (RFS) were compared by hazard ratio (HR) and 95% CIs. A total of 19 RCTs were included in our meta-analysis, among which 2,501 patients were treated with PBAT and 2,290 with non-PBAT. The patients treated with PBAT combined a significantly higher pCR rate compared to those patients treated with non-PBAT (49.8% versus 36.4%, OR = 1.27, 95%CI = 1.14-1.43, P < 0.001). Besides, patients treated with PBAT had a significantly better RFS (HR = 0.78, 95%CI = 0.63-0.95, P = 0.016), but not in OS (HR = 0.84, P = 0.304). Although the occurrence of neutropenia and nausea were slightly different between the PBAT group (51.5% and 24.4%) and the non-PBAT group (47.0% and 29.4%), the complications were acceptable in the two treatments groups. Our results demonstrated that TNBC patients treated with PBAT could achieve a higher pCR rate and better RFS benefit without a higher complication rate.Highlights Platinum-based adjuvant therapy provided a higher pCR rate for TNBC.Platinum-based adjuvant therapy prolonged the RFS but without prolongingthe OS.Neutropenia and nausea rate was different between group PBAT and non-PBAT.
Keywords: neoadjuvant therapy; platinum; survival; triple-negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

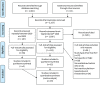

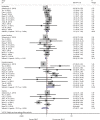
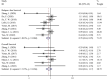
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of platinum-based and non-platinum-based drugs on triple-negative breast cancer: meta-analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Oct 15;27(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00839-0. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 36242046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Oncol. 2018 Jul 1;29(7):1497-1508. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy127. Ann Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29873695
-
Triple negative breast cancer and platinum-based systemic treatment: a meta-analysis and systematic review.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 8;19(1):1065. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6253-5. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31703646 Free PMC article.
-
Platinum-based chemotherapy in early-stage triple negative breast cancer: A meta-analysis.Cancer Treat Rev. 2021 Nov;100:102283. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102283. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021. PMID: 34530283
-
The Impact of Platinum-Containing Chemotherapies in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Meta-Analytical Approach to Evaluating Its Efficacy and Safety.Oncol Res Treat. 2021;44(6):333-343. doi: 10.1159/000515353. Epub 2021 May 11. Oncol Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 33975311
Cited by
-
PinX1 plays multifaceted roles in human cancers: a review and perspectives.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Nov 17;51(1):1163. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10082-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39550726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential mechanism of HIF-1α and CD147 in the development of triple-negative breast cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jun 7;103(23):e38434. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038434. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38847725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L, et al. Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(1):52–62. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A.. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5. - PubMed
-
- Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:4429–4434. - PubMed
-
- Foulkes WD, Smith IE, Reis-Filho JS. Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1938–1948. - PubMed
-
- Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, et al. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J clin oncol. 2008;26:1275–1281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
