Real-world experience of secukinumab in moderate to severe psoriasis patients in Thailand: Characteristics, effectiveness, and safety
- PMID: 36279306
- PMCID: PMC10078165
- DOI: 10.1111/dth.15958
Real-world experience of secukinumab in moderate to severe psoriasis patients in Thailand: Characteristics, effectiveness, and safety
Abstract
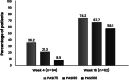
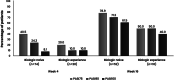
Secukinumab demonstrated high efficacy and favorable safety profile in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis (PsO) in clinical trials. However, understanding of patient characteristics and clinical outcomes in real world in Thailand is still limited. To describe patient characteristics, effectiveness and safety of secukinumab in Thai PsO patients. This retrospective study analyzed data from medical records of adult PsO patients who initiated secukinumab at 7 dermatology centers from September 2017 to April 2021. Study outcomes included patient characteristics and changes in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score from baseline at weeks 4 and 16 after secukinumab initiation. Adverse events were recorded. Subgroup analyses by adherence rate and completeness of loading dose were performed. Of 163 patients, the mean (SD) age was 44.0 (14.0) years. Most patients (84.7%) were previously treated with topical therapy while 62.0% and 21.5% of patients had received systemic and biologic therapy, respectively. The mean baseline PASI score was 15.4 (9.3). Overall, the mean PASI score improved by 58.0% at week 4 and 78.4% at week 16. Statistically significant differences in PASI approvement were revealed among subgroups of patients with different loading dose and adherence rate. Adverse effects were reported in 8.0% of patients. The characteristics of patients in this study were slightly different from clinical trials in terms of demographic and clinical characteristics, as well as PsO treatment. Secukinumab was effective and safe in Thai patients with PsO, especially among those with complete loading dose and a higher adherence rate.
Keywords: IL-17; biologics; psoriasis; real world; secukinumab.
© 2022 The Authors. Dermatologic Therapy published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Asawanonda received honoraria for lecturing and research grant for Novartis, Zeullig Pharma, Kyowa Kirin, Janssen, and Leo Pharma. Dr. Pattamadilok received research grant and has served as a principal investigator, and an advisory board member for Novartis, Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Chularojanamontri has served as paid speaker for Novartis, Janssen, and Zeullig Pharma. Dr. Chuamanochan received honoraria for lecturing for Novartis, Leo Pharma, and Janssen. Dr. Choonhakarn has served as paid speaker for Novartis, Janssen, Menarini, Beiersdof, Galderma, Zuellig Pharma, Takeda, MSD, GSK, and BeRich. Dr. Chakkavittumrong has served as paid speaker, and received research grant for Novartis, Zuellig Pharma, Janssen, Galderma, and IQVIA. Dr. Rajatanavin has served as paid speaker, and principal investigator for Novartis, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Ms. Sangob is a medical lead in Novartis.
Figures
References
-
- Martínez‐Ortega JM, Nogueras P, Muñoz‐Negro JE, Gutiérrez‐Rojas L, González‐Domenech P, Gurpegui M. Quality of life, anxiety and depressive symptoms in patients with psoriasis: a case‐control study. J Psychosom Res. 2019;124:109780. - PubMed
-
- Thakolwiboon S, Upala S, Geeratragool T, et al. The factors affecting quality of life in Thai psoriasis patients. J Med Assoc Thai. 2013;96(10):1344‐1349. - PubMed
-
- Unaeze J, Nijsten T, Murphy A, Ravichandran C, Stern RS. Impact of psoriasis on health‐related quality of life decreases over time: an 11‐year prospective study. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126(7):1480‐1489. - PubMed
-
- Augustin M, Krüger K, Radtke MA, Schwippl I, Reich K. Disease severity, quality of life and health care in plaque‐type psoriasis: a multicenter cross‐sectional study in Germany. Dermatology. 2008;216(4):366‐372. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous