NVX-CoV2373-induced cellular and humoral immunity towards parental SARS-CoV-2 and VOCs compared to BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273-regimens
- PMID: 36279695
- PMCID: PMC9576915
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2022.105321
NVX-CoV2373-induced cellular and humoral immunity towards parental SARS-CoV-2 and VOCs compared to BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273-regimens
Abstract
Background: The NVX-CoV2373-vaccine has recently been licensed, although knowledge on vaccine-induced humoral and cellular immunity towards the parental strain and variants of concern (VOCs) in comparison to mRNA-regimens is limited.
Methods: In this observational study, 66 individuals were recruited to compare immunogenicity and reactogenicity of NVX-CoV2373 with BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273. Vaccine-induced antibodies were analyzed using ELISA and neutralization assays, specific CD4 and CD8 T-cells were characterized based on intracellular cytokine staining using flow-cytometry after antigen-specific stimulation with parental spike or VOCs.
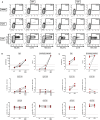
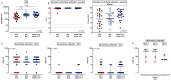
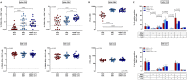
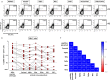
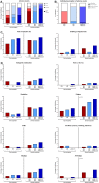
Results: Two doses of NVX-CoV2373 strongly induced anti-spike IgG, although IgG-levels were lower than after vaccination with BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 (p = 0.006). Regardless of the vaccine and despite different IgG-levels, neutralizing activity towards VOCs was highest for Delta, followed by BA.2 and BA.1. The protein-based vaccine failed to induce any spike-specific CD8 T-cells which were detectable in 3/22 (14%) individuals only. In contrast, spike-specific CD4 T-cells were induced in 18/22 (82%) individuals, although their levels were lower (p<0.001), had lower CTLA-4 expression (p<0.0001) and comprised less multifunctional cells co-expressing IFNγ, TNFα and IL-2 (p = 0.0007). Unlike neutralizing antibodies, NVX-CoV2373-induced CD4 T-cells equally recognized all tested VOCs from Alpha to Omicron. In individuals with a history of infection, one dose of NVX-CoV2373 had similar immunogenicity as two doses in non-infected individuals. The vaccine was overall well tolerated.
Conclusion: NVX-CoV2373 strongly induced spike-specific antibodies and CD4 T-cells, albeit at lower levels as mRNA-regimens. Cross-reactivity of CD4 T-cells towards the parental strain and all tested VOCs may hold promise to protect from severe disease.
Keywords: Antibodies; COVID-19; Coronavirus; Neutralization; SARS-CoV-2; T-cells; Vaccination; Variant of concern.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest M.S. has received grant support from Astellas and Biotest to the organization Saarland University outside the submitted work, and honoraria for lectures from Biotest and Novartis. M.W. has received speaker fees from Astra Zeneca and grant support from Roche Molecular Diagnostics to the organization Goethe University Frankfurt outside the submitted work. All other authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- European Medicine Agency (EMA). EMA recommends nuvaxovid for authorisation in the EU. 2021 20th december 2021 [cited; Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/ema-recommends-nuvaxovid-authorisation-eu.
-
- Ständige Impfkommission Aktualisierung der COVID-19-impfempfehlung. Epid. Bull. 2022;7:3–18.
-
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA). Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA authorizes emergency use of novavax COVID-19 vaccine, adjuvanted. 2022 13th july [cited; Available from: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-COVID-19....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

