A peptide array pipeline for the development of Spike-ACE2 interaction inhibitors
- PMID: 36279985
- PMCID: PMC9585897
- DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2022.170898
A peptide array pipeline for the development of Spike-ACE2 interaction inhibitors
Abstract
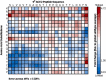
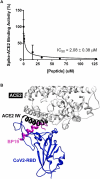
In humans, coronaviruses are the cause of endemic illness and have been the causative agents of more severe epidemics. Most recently, SARS-CoV-2 was the causative agent of the COVID19 pandemic. Thus, there is a high interest in developing therapeutic agents targeting various stages of the coronavirus viral life cycle to disrupt viral propagation. Besides the development of small-molecule therapeutics that target viral proteases, there is also interest molecular tools to inhibit the initial event of viral attachment of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein to host ACE2 surface receptor. Here, we leveraged known structural information and peptide arrays to develop an in vitro peptide inhibitor of the Spike-ACE2 interaction. First, from previous co-crystal structures of the Spike-ACE2 complex, we identified an initial 24-residue long region (sequence: STIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQ) on the ACE2 sequence that encompasses most of the known contact residues. Next, we scanned this 24-mer window along the ACE2 N-terminal helix and found that maximal binding to the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (CoV2-RBD) was increased when this window was shifted nine residues in the N-terminal direction. Further, by systematic permutation of this shifted ACE2-derived peptide we identified mutations to the wildtype sequence that confer increased binding of the CoV2-RBD. Among these peptides, we identified binding peptide 19 (referred to as BP19; sequence: SLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFI) as an in vitro inhibitor of the Spike-ACE2 interaction with an IC50 of 2.08 ± 0.38 μM. Overall, BP19 adds to the arsenal of Spike-ACE2 inhibitors, and this study highlights the utility of systematic peptide arrays as a platform for the development of coronavirus protein inhibitors.
Keywords: ACE2; Peptide array; Peptide inhibitor; Spike.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhong N.S., Zheng B.J., Li Y.M., Poon L.L.M., Xie Z.H., Chan K.H., Li P.H., Tan S.Y., Chang Q., Xie J.P., et al. Epidemiology and cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong, People’s Republic of China, in February, 2003. Lancet. 2003;362:1353. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14630-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

