Synaptotagmins 1 and 7 in vesicle release from rods of mouse retina
- PMID: 36280223
- PMCID: PMC9830644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.109279
Synaptotagmins 1 and 7 in vesicle release from rods of mouse retina
Abstract
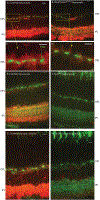
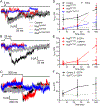
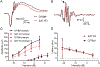
Synaptotagmins are the primary Ca2+ sensors for synaptic exocytosis. Previous work suggested synaptotagmin-1 (Syt1) mediates evoked vesicle release from cone photoreceptor cells in the vertebrate retina whereas release from rods may involve another sensor in addition to Syt1. We found immunohistochemical evidence for syntaptotagmin-7 (Syt7) in mouse rod terminals and so performed electroretinograms (ERG) and single-cell recordings using mice in which Syt1 and/or Syt7 were conditionally removed from rods and/or cones. Synaptic release was measured in mouse rods by recording presynaptic anion currents activated during glutamate re-uptake and from exocytotic membrane capacitance changes. Deleting Syt1 from rods reduced glutamate release evoked by short depolarizing steps but not long steps whereas deleting Syt7 from rods reduced release evoked by long but not short steps. Deleting both sensors completely abolished depolarization-evoked release from rods. Effects of various intracellular Ca2+ buffers showed that Syt1-mediated release from rods involves vesicles close to ribbon-associated Ca2+ channels whereas Syt7-mediated release evoked by longer steps involves more distant release sites. Spontaneous release from rods was unaffected by eliminating Syt7. While whole animal knockout of Syt7 slightly reduced ERG b-waves and oscillatory potentials, selective elimination of Syt7 from rods had no effect on ERGs. Furthermore, eliminating Syt1 from rods and cones abolished ERG b-waves and additional elimination of Syt7 had no further effect. These results show that while Syt7 contributes to slow non-ribbon release from rods, Syt1 is the principal sensor shaping rod and cone inputs to bipolar cells in response to light flashes.
Keywords: Cones; Electroretinogram; Exocytosis; Mouse; Neuroscience; Retina; Ribbon synapse; Rods.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Ca2+ sensor synaptotagmin-1 mediates exocytosis in mammalian photoreceptors.Elife. 2019 Jun 7;8:e45946. doi: 10.7554/eLife.45946. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31172949 Free PMC article.
-
Control of exocytosis by synaptotagmins and otoferlin in auditory hair cells.J Neurosci. 2010 Oct 6;30(40):13281-90. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2528-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20926654 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin-9 in mouse retina.Vis Neurosci. 2024 Sep 18;41:E003. doi: 10.1017/S0952523824000026. Vis Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39291699 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission at rod and cone ribbon synapses in the retina.Pflugers Arch. 2021 Sep;473(9):1469-1491. doi: 10.1007/s00424-021-02548-9. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Pflugers Arch. 2021. PMID: 33779813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinetics of synaptic transmission at ribbon synapses of rods and cones.Mol Neurobiol. 2007 Dec;36(3):205-23. doi: 10.1007/s12035-007-0019-9. Epub 2007 Jul 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17955196 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Three-Dimensional Ultrastructure of the Normal Rod Photoreceptor Synapse and Degenerative Changes Induced by Retinal Detachment.J Neurosci. 2023 Jul 26;43(30):5468-5482. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2267-22.2023. Epub 2023 Jul 6. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37414561 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term plasticity and context-dependent circuit function: Insights from retinal circuitry.Sci Adv. 2024 Sep 20;10(38):eadp5229. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adp5229. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39303044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using optogenetics to dissect rod inputs to OFF ganglion cells in the mouse retina.Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2023;3:1146785. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2023.1146785. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37426783 Free PMC article.
-
The Structural and Functional Integrity of Rod Photoreceptor Ribbon Synapses Depends on Redundant Actions of Dynamins 1 and 3.J Neurosci. 2024 Jun 19;44(25):e1379232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1379-23.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38641407 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic Proteins and Their Roles in Visual Processing by the Retina.Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2024 Sep;10(1):347-375. doi: 10.1146/annurev-vision-101322-111204. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38621251 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bourgeois-Jaarsma Q, Miaja Hernandez P, Groffen AJ, 2021. Ca(2+) sensor proteins in spontaneous release and synaptic plasticity: limited contribution of Doc2c, rabphilin-3a and synaptotagmin 7 in hippocampal glutamatergic neurons. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 112, 103613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

