The Absence of Parkin Does Not Promote Dopamine or Mitochondrial Dysfunction in PolgAD257A/D257A Mitochondrial Mutator Mice
- PMID: 36280265
- PMCID: PMC9761676
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0545-22.2022
The Absence of Parkin Does Not Promote Dopamine or Mitochondrial Dysfunction in PolgAD257A/D257A Mitochondrial Mutator Mice
Abstract
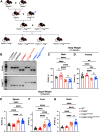
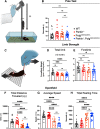
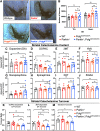
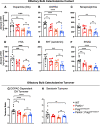
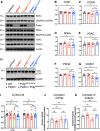
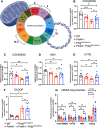
Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized by the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc). In this study, we generated a transgenic model by crossing germline Parkin-/- mice with PolgAD257A mice, an established model of premature aging and mitochondrial stress. We hypothesized that loss of Parkin-/- in PolgAD257A/D257A mice would exacerbate mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to loss of dopamine neurons and nigral-striatal specific neurobehavioral motor dysfunction. We found that aged Parkin-/-/PolgAD257A/D257A male and female mice exhibited severe behavioral deficits, nonspecific to the nigral-striatal pathway, with neither dopaminergic neurodegeneration nor reductions in striatal dopamine. We saw no difference in expression levels of nuclear-encoded subunits of mitochondrial markers and mitochondrial Complex I and IV activities, although we did observe substantial reductions in mitochondrial-encoded COX41I, indicating mitochondrial dysfunction as a result of PolgAD257A/D257A mtDNA mutations. Expression levels of mitophagy markers LC3I/LC3II remained unchanged between cohorts, suggesting no overt mitophagy defects. Expression levels of the parkin substrates, VDAC, NLRP3, and AIMP2 remained unchanged, suggesting no parkin dysfunction. In summary, we were unable to observe dopaminergic neurodegeneration with corresponding nigral-striatal neurobehavioral deficits, nor Parkin or mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkin-/-/PolgAD257A/D257A mice. These findings support a lack of synergism of Parkin loss on mitochondrial dysfunction in mouse models of mitochondrial deficits.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Producing a mouse model of Parkinson's disease (PD) that is etiologically relevant, recapitulates clinical hallmarks, and exhibits reproducible results is crucial to understanding the underlying pathology and in developing disease-modifying therapies. Here, we show that Parkin-/-/PolgAD257A/D257A mice, a previously reported PD mouse model, fails to reproduce a Parkinsonian phenotype. We show that these mice do not display dopaminergic neurodegeneration nor nigral-striatal-dependent motor deficits. Furthermore, we report that Parkin loss does not synergize with mitochondrial dysfunction. Our results demonstrate that Parkin-/-/PolgAD257A/D257A mice are not a reliable model for PD and adds to a growing body of work demonstrating that Parkin loss does not synergize with mitochondrial dysfunction in mouse models of mitochondrial deficits.
Keywords: POLG; Parkinson's disease; mitochondria; mitophagy; parkin.
Copyright © 2022 the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lack of Parkin Anticipates the Phenotype and Affects Mitochondrial Morphology and mtDNA Levels in a Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease.J Neurosci. 2018 Jan 24;38(4):1042-1053. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1384-17.2017. Epub 2017 Dec 8. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29222404 Free PMC article.
-
Accumulation of mitochondrial DNA deletions within dopaminergic neurons triggers neuroprotective mechanisms.Brain. 2013 Aug;136(Pt 8):2369-78. doi: 10.1093/brain/awt196. Brain. 2013. PMID: 23884809
-
Manganese exposure exacerbates progressive motor deficits and neurodegeneration in the MitoPark mouse model of Parkinson's disease: Relevance to gene and environment interactions in metal neurotoxicity.Neurotoxicology. 2018 Jan;64:240-255. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Neurotoxicology. 2018. PMID: 28595911 Free PMC article.
-
RGS Proteins as Critical Regulators of Motor Function and Their Implications in Parkinson's Disease.Mol Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;98(6):730-738. doi: 10.1124/mol.119.118836. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Mol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32015009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in genetic animal models of Parkinson's disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 May 1;16(9):896-919. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4200. Epub 2011 Oct 4. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 21848447 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution and maintenance of mtDNA gene content across eukaryotes.Biochem J. 2024 Aug 7;481(15):1015-1042. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20230415. Biochem J. 2024. PMID: 39101615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of PINK1-Parkin in mitochondrial quality control.Nat Cell Biol. 2024 Oct;26(10):1639-1651. doi: 10.1038/s41556-024-01513-9. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Nat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39358449 Review.
-
PINK1 regulated mitophagy is evident in skeletal muscles.Autophagy Rep. 2024 Mar 11;3(1):2326402. doi: 10.1080/27694127.2024.2326402. Autophagy Rep. 2024. PMID: 38988500 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial DNA Instability Supersedes Parkin Mutations in Driving Mitochondrial Proteomic Alterations and Functional Deficits in Polg Mutator Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 11;25(12):6441. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126441. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928146 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting mitophagy in neurodegenerative diseases.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025 Apr;24(4):276-299. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-01105-0. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025. PMID: 39809929 Review.
References
-
- Andres-Mateos E, Perier C, Zhang L, Blanchard-Fillion B, Greco TM, Thomas B, Ko HS, Sasaki M, Ischiropoulos H, Przedborski S, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2007) DJ-1 gene deletion reveals that DJ-1 is an atypical peroxiredoxin-like peroxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:14807–14812. 10.1073/pnas.0703219104 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
